FIG 1.
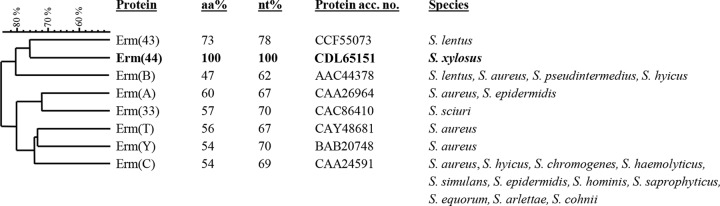
Relatedness of erythromycin resistance methylases (Erm proteins) of different Staphylococcus species. Amino acid and nucleotide sequence identity percentages were obtained by sequence alignment with ClustalW (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/). The sequences chosen for comparison are from the species for which the Erm protein was initially described. Clustering of Erm amino acid sequences was performed by BioNumerics 7.1 (Applied Maths). The comparison settings were standard algorithm for pairwise alignment, an open gap penalty of 100%, a unit gap penalty of 0%, and the unweighted-pair group method using average linkages. Methylase genes that were detected in Staphylococcus only by PCR and/or hybridization and for which sequences are not available [e.g., erm(F), erm(G), erm(Q)] were not included (http://faculty.washington.edu/marilynr/).
