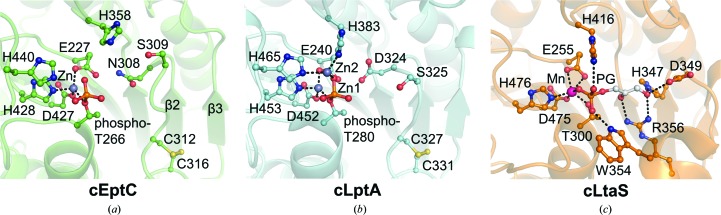
Figure 4.
Juxtaposed active sites of (a) cEptC, (b) cLptA (PDB entry 4kay) and (c) S. aureus cLtaS (PDB entry 2w5s). Active-site architectures and zinc-binding residues are conserved between cEptC and cLptA (Supplementary Fig. S6), although only one Zn2+ ion associates with cEptC in crystallo. His358/His383 and metal-ligand residues of cEptC and cLptA are also conserved in cLtaS. Side chains on an active-site loop/helix of cLtaS, corresponding to a loop between β2 and β3 of cEptC, bind phosphoglycerol (PG, white C atoms; Lu et al., 2009 ▶). In cEptC and cLptA, this loop contains Asn308/Asp324 and Ser309/Ser325, which may contribute to substrate binding. Notably, Thr266, His358, His440, Asn308 and Ser309 mutant strains of eptC in C. jejuni displayed polymyxin B sensitivity and a severe loss of motility (Figs. 5 ▶ and 6 ▶).