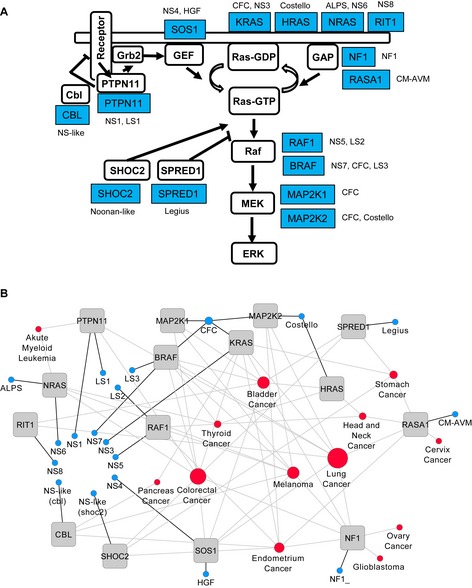
Diseasome of RASopathies and cancer. Each node corresponds to a distinct disorder or cancer type. The size of the node corresponds to the total number of genes (among the 15 genes) that are involved in a particular disease. Abbreviations: NS, Noonan syndrome; NF1, neurofibromatosis type 1; CFC, cardiofaciocutaneous; LS, LEOPARD syndrome; HGF, hereditary gingvial fibromatosis; CM‐AVM, capillary malfunction‐arteriovenous malfunction; ALPS, autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome. Suffixes in NS (NS1, NS3, NS4, NS5, NS6, NS7, NS8 and NS‐like) and LS (LS1 to LS3) are different forms of the respective disease according to the classification in the OMIM database.