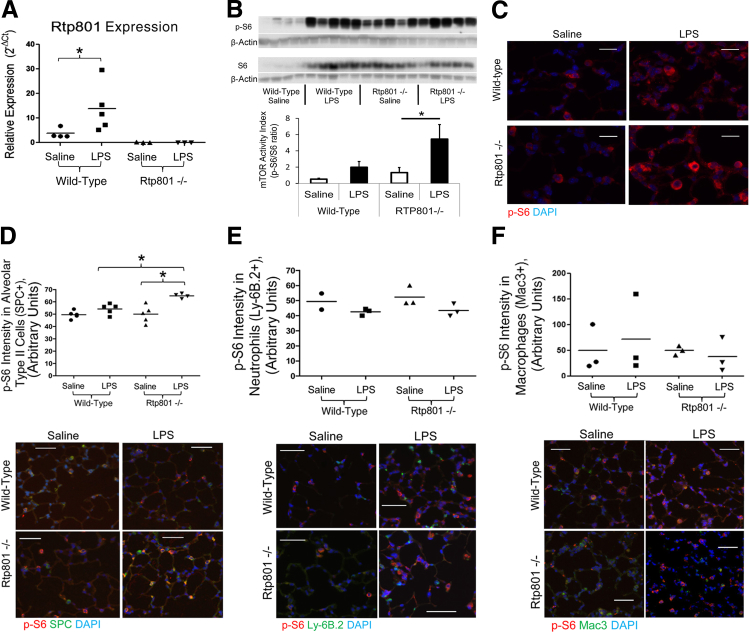
Figure 1.
Rtp801 suppresses LPS activation of epithelial mTORC1. A: Four hours after 2 mg/kg intratracheal LPS, pulmonary expression of Rtp801 is significantly increased in WT mice, as assessed by qPCR. Rtp801 expression is absent in Rtp801−/− mice. Expression is quantified as 2−ΔCT, normalized to the housekeeping gene cyclophilin A. Pulmonary mTORC1 activity (assessed by the relative phosphorylation of the mTORC1 target ribosomal S6, p-S6) increases nonsignificantly 4 hours after 2 mg/kg intratracheal LPS, as assessed by Western blot analysis of lung homogenates (B) and lung immunofluorescence (C). In the absence of Rtp801, LPS significantly increases pulmonary mTORC1 activity, demonstrating that Rtp801 induction functions to suppress LPS activation of pulmonary mTORC1. Immunofluorescent colocalization demonstrates that loss of Rtp801 augments mTORC1 signaling (p-S6) within alveolar type II epithelial cells (SPC positive, D) 4 hours after 2 mg/kg intratracheal LPS. No increase in p-S6 is noted within neutrophils (E) or macrophages (F). Red, p-S6; blue, DAPI; green, SPC (D), Ly-6B.2 (neutrophil marker, E), or Mac3 (macrophage marker, F); yellow, colocalization. ∗P < 0.05. n = 3 to 5 per group, except WT saline Ly-6B.2 (n = 2). Scale bars: 10 μm (C); 50 μm (D–F).