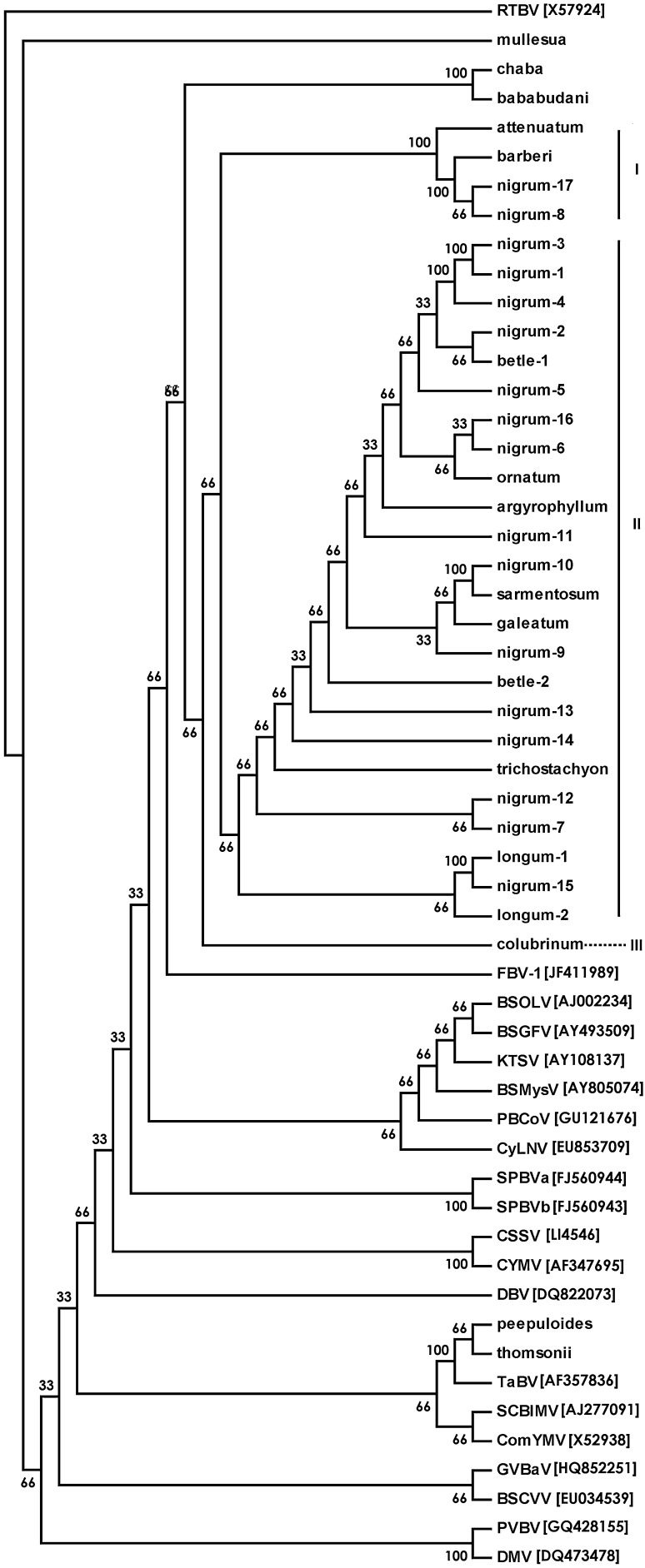
Fig. 1.
Consensus tree generated using consense in the Phylip package with Neighbor joining, Bayesian, Maximum Likelihood and Maximum Parsimony methods based on the multiple alignment of the deduced amino acid sequences of RT/RNaseH region of badnavirus isolates from black pepper and related species with known badnaviruses. Details of the badnavirus isolates from Piper species and their GenBank accession number is provided in Table 1. Corresponding sequences from other badnavirus species used were retrieved from GenBank, their acronym and accession number is indicated in the figure. BSGFV Banana streak GF virus, BSMysV Banana streak Mysore virus, BSOLV Banana streak OL virus, BSCVV Bougainvillea spectabilis chlorotic vein-banding virus, CSSV Cacao swollen shoot virus, CYMV Citrus yellow mosaic virus, ComYMV Commelina yellow mottle virus, CyLNV Cycad leaf necrosis virus, DBV Dioscorea bacilliform virus, DMV Dracaena mottle virus, FBV-1 Fig badnavirus 1, GVBaV Gooseberry vein banding virus, KTSV Kalanchoe top-spotting virus, PVBV Pelargonium vein banding virus, SCBIMV Sugarcane bacilliform IM virus, SPBVa Sweetpotato badnavirus A, SPBVb Sweetpotato badnavirus B, TaBV Taro bacilliform virus. Rice tungro bacilliform virus (RTBV) was taken as outgroup. Bootstrap values are shown at the nodes