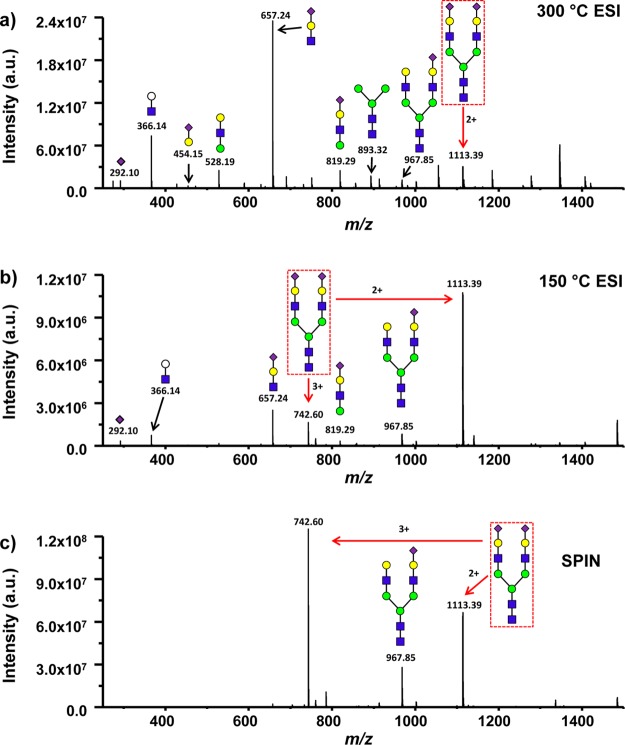
Figure 6.
Mass spectra of an N-glycan containing sialic acid, Hex5HexNAc4NeuAc2 (2224.01 Da), from the LC–MS analysis of human serum obtained from the conventional ESI-MS interface operated with capillary inlet temperatures of 300 °C (a) and 150 °C (b), and for the SPIN interface (c). The red arrows represent the 3+ and 2+ charge states of the observed intact glycan. Consortium for functional glycomics (CFG) nomenclature was used to illustrate putative glycan structure with each sugar type denoted by a shape and isomers differentiated by color. Yellow and green circles represent hexoses with galactose and mannose stereochemistries, respectively, blue squares represent N-acetylhexosamine with glucose stereochemistry, and purple diamonds represent N-acetylneuraminic acid (sialic acid). White circles were used as a modification to represent a generic hexose.