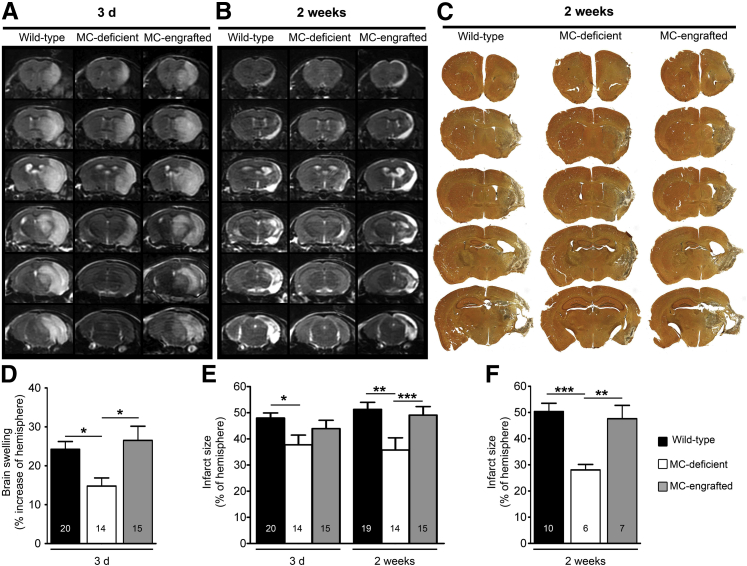
Figure 1.
MCs can contribute to infarct size and brain swelling after stroke. Representative T2W-MRI of brains of WT (WBB6F1-Kit+/+) mice, MC-deficient (WBB6F1-KitW/W-v) mice, and MC-engrafted (WBB6F1-Kit+/+ BMCMCs→WBB6F1-KitW/W-v) mice at 3 days (A) or 2 weeks (B) after stroke. C: Representative silver-stained serial coronal sections of brains of WT, MC-deficient, and MC-engrafted mice at 2 weeks after stroke. Quantification from T2W-MRI scans of brain swelling at 3 days (D) and infarct size at 3 days and 2 weeks (E) after stroke. F: Quantification of infarct size from brain sections obtained 2 weeks after stroke. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (D–F). Data were pooled from eight (E) and three (F) experiments, each of which gave similar results. The number of mice in each group is indicated in each bar. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.005.