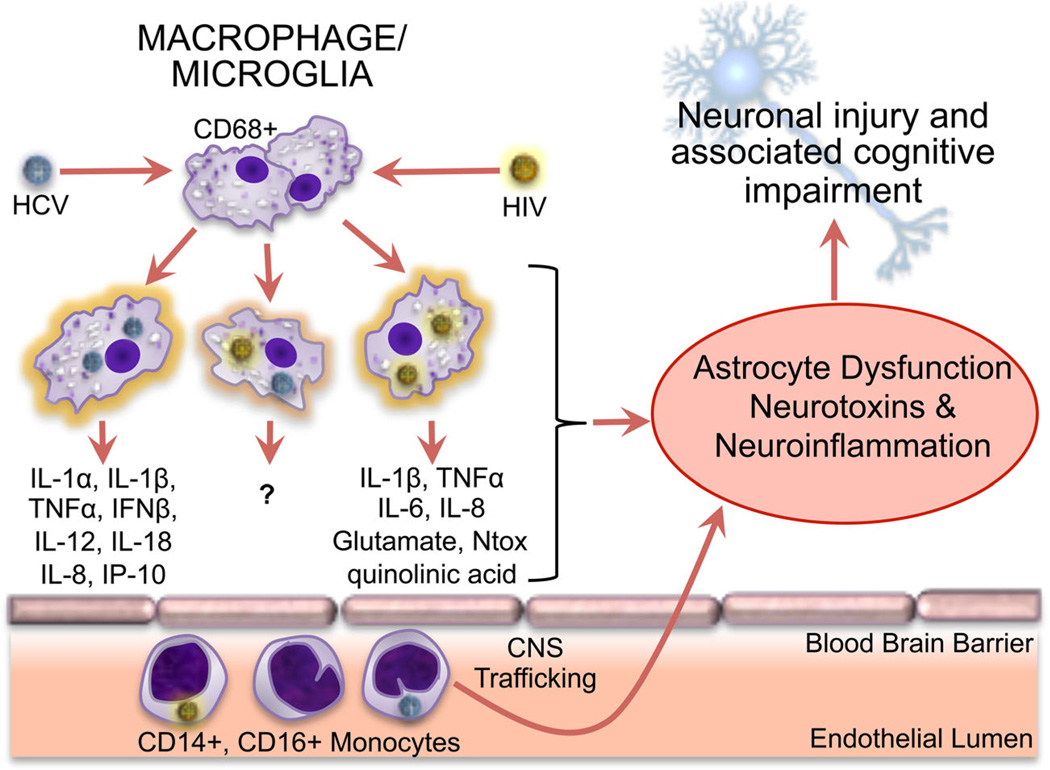
Fig. 1.
CNS inflammatory effects of HIV and HCV infection of monocytes, macrophages, and microglia. CD14+/CD16+ monocytes can be infected by HCV and HIV and migrate across the endothelial barrier into the brain. Macrophages and microglia within the brain can support productive infection with HIV and HCV, resulting in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and neurotoxins (glutamate, Ntox, quinolinic acid). Those associated with HCV infection are depicted in the left-most macrophage image, and those associated with HIV infection are depicted in the right-most macrophage image. Such pro-inflammatory cytokines and neurotoxins have been shown to induce neuronal injury through direct and indirect (astrocyte-mediated) mechanisms