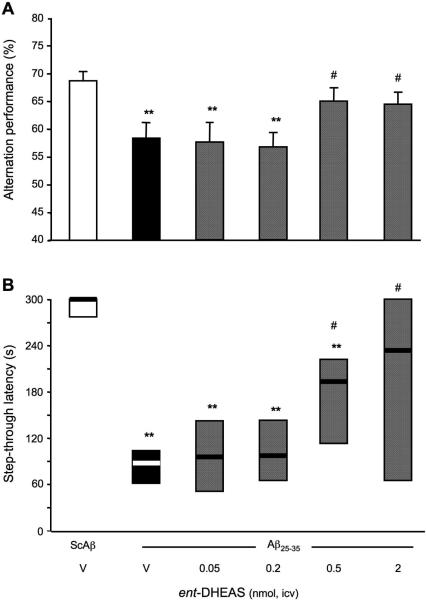
Figure 13.
Protective effects of ent-DHEAS against the Aβ25-35 peptide-induced memory deficits in mice: (A) spontaneous alternation performances; and (B) step-through passive avoidance. Mice were administered i.c.v. with distilled water (V) or ent-DHEAS (0.05-2 nmol) simultaneously with Aβ25-35 peptide (9 nmol). The i.c.v. injection of ScAβ (9 nmol) was used as control. Spontaneous alternation performances in the Y-maze were measured on day 7. Passive avoidance training was carried out on day 8 and retention on day 9. F(5,94) = 3.86, p < 0.01, n = 10, in (A), H = 15.3, p < 0.01, n = 12, in (B). ** p < 0.01 vs. the (ScAβ+V)-treated group; # p < 0.05 vs. the (Aβ25-35+V)-treated group; Dunnett's test in (A), Dunn's test in (B).