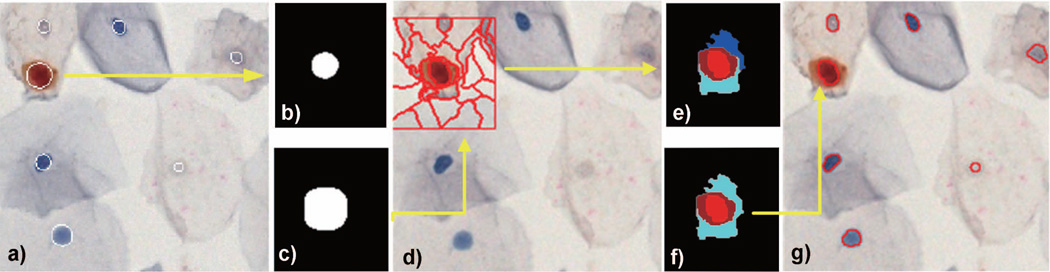
Figure 5.
Superpixels segmentation, classification and merging in Pap smear images: (a) computed RDS-based nuclear mask superimposed on the digital image, b) RSD-based mask of a p16+/Ki67+ nucleus, c) dilated RSD-based mask, d) window W around the dilated mask split into superpixels, e) the k-nn classification was used to assign superpixels to nuclear (red) and cytoplasmic (cyan, blue and brown) locations, f) non-circular and non-convex superpixels were removed and the boundary of the remaining superpixel were superimposed on the digital image (g). Note the difference between the RSD-based mask – nuclei approximated by circles in a) and the fine boundary of nuclear contour in g) which better represents the location of boundary between the nuclear envelope and the cytoplasm.