Table 4. Ridge-regression vs lasso.
| par. | obs. stat. | p-value |
sample size ( ) ) |
28.003 | <0.001 |
number of features (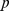 ) ) |
99.312 | <0.001 |
saturation (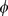 ) ) |
78.062 | <0.001 |
signal-to-noise (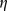 ) ) |
0.949 | 0.541 |
correlation (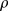 ) ) |
85.745 | <0.001 |
sample size vs number of features (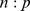 ) ) |
3.948 | <0.001 |
sample size vs saturation (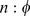 ) ) |
8.321 | <0.001 |
sample size vs signal-to-noise (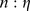 ) ) |
1.002 | 0.482 |
sample size vs correlation (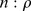 ) ) |
0.996 | 0.490 |
number of features vs saturation (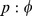 ) ) |
41.886 | <0.001 |
number of features vs signal-to-noise (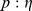 ) ) |
1.023 | 0.426 |
number of features vs correlation (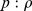 ) ) |
1.393 | 0.017 |
saturation vs signal-to-noise (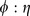 ) ) |
1.017 | 0.443 |
saturation vs correlation (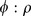 ) ) |
0.570 | 1.000 |
signal-to-noise vs correlation ( ) ) |
0.695 | 0.986 |
Permutation tests for equality of the group distributions using distance components analysis (lines 2 to 6), and permutation F-tests for the presence of 2-by-2 interactions (lines 7 to 16), in the comparison of ridge-regression vs lasso. Results based on 999 permutations.
