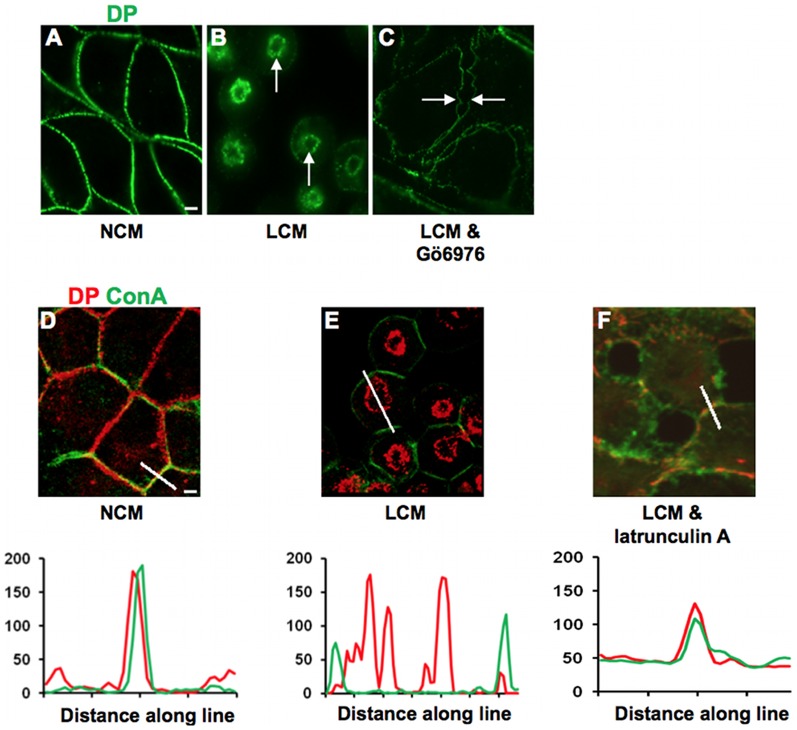
Figure 1. Half desmosome internalisation is cPKC and actin dependent.
(A) MDCK cells cultured in NCM had desmosomes at cell-cell contacts as indicated by DP staining. (B) Internalised rings of DP were present in cells treated for 60 minutes with LCM (arrows). (All internalisation controls in LCM were carried out in the presence of the appropriate drug vehicle.) (C) Internalisation of desmosomes was prevented by co-treatment with LCM and Gö6976 (0.8 µM), as cell contact was lost but half desmosomes remained at the cell surface giving rise to the appearance of intercellular gaps (arrows). (D) In NCM, DP (red) was localised to the cell surface in association with the surface marker con-A (green). (E) LCM treatment caused internalisation of DP and separation from con-A, which remained at the surface. (F) Co-treatment with LCM and latrunculin A (5 µM) inhibited desmosome internalisation, as indicated by persistent association of DP with con-A. Fluorescence profiles depict the intensity of staining along the white line in the images.