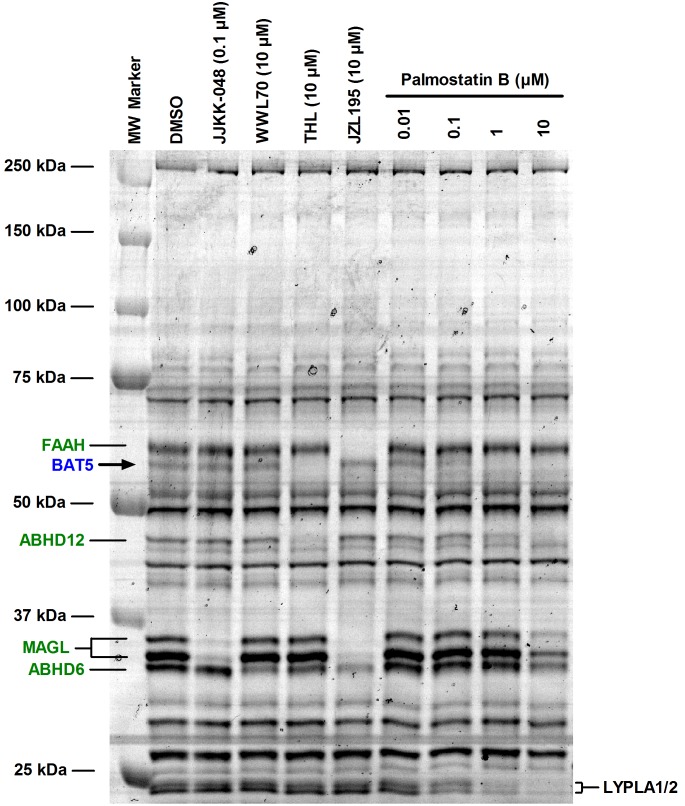
Figure 8. Competitive ABPP unveiling palmostatin B targets among the serine hydrolases in mouse brain membrane proteome.
Membranes (100 µg) were pretreated for 1 h with DMSO or the indicated concentrations of the serine hydrolase inhibitors, after which TAMRA-FP labelling was conducted for 1 hour at RT. The reaction was stopped, 10 µg protein (10 µl) was loaded per lane and the proteins were separated in SDS-electrophoresis gel (10%). TAMRA-FP labeling was visualized after in-gel fluorescence imaging as described in the Methods section. Molecular weight markers are indicated at left. Reference inhibitors JJKK-048, WWL70, THL and JZL195 were used at the indicated concentrations to identify the following serine hydrolases from the gel: fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), inhibited by JZL195 [21]; MAGL doublet, inhibited by JJKK-048 [22] and JZL195 [21]; ABHD6, inhibited by WWL70 [23]–[24], THL [18], and also by JZL195 at the used concentration; BAT5, inhibited by THL [4], [18]. Note that palmostatin B dose-dependently inhibits probe labeling of BAT5, ABHD12 and LYPLA1/2, two closely-related proteins migrating at ∼25 kDa [25]. At the highest concentration, probe labeling of MAGL and ABHD6 is also inhibited. Note the absence of additional visible targets for palmostatin B at the tested concentrations. Data are representative from three ABPP experiments with similar outcome.