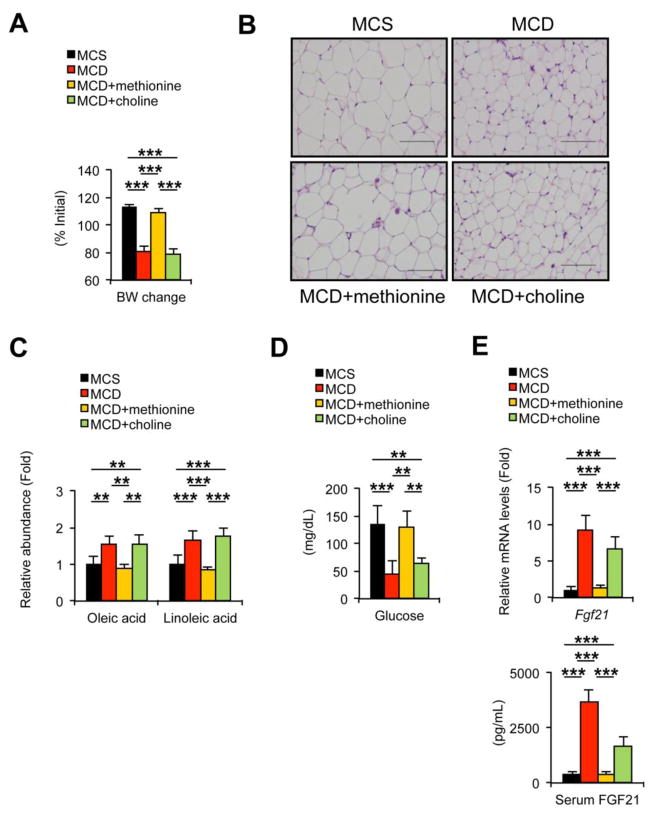
Fig. 4. Increases in serum oleic and linoleic acids and changes in WAT by MCD treatment are reversed by methionine supplementation.
Male C57BL/6NCr wild-type mice at 8–12 weeks of age were treated with MCS with drinking deionized water, MCD with drinking deionized water, MCD with drinking deionized water containing L-methionine (4 mg/mL, MCD+methionine), or MCD with drinking deionized water containing choline bitartrate (30 mg/mL, MCD+choline) for two weeks (n = 5/group) and serum, liver, and epididymal WAT were collected.
(A) Body weight (BW) change. Values were expressed as the percentage relative to BW just before commencing the MCD or MCS treatment.
(B) Histology of epididymal WAT. Hematoxylin and eosin staining, Bar = 100 μm.
(C) Serum levels of oleic and linoleic acids. Values were normalized to those of MCS-treated mice and were expressed as relative abundance.
(D) Serum glucose concentrations.
(E) Hepatic Fgf21 mRNA levels and serum FGF21 concentrations. The mRNA levels were normalized to those of 18S ribosomal mRNA and subsequently normalized to those of MCS-treated mice.
Statistical analysis was performed using the one-way ANOVA test with Bonferroni’s correction. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001.