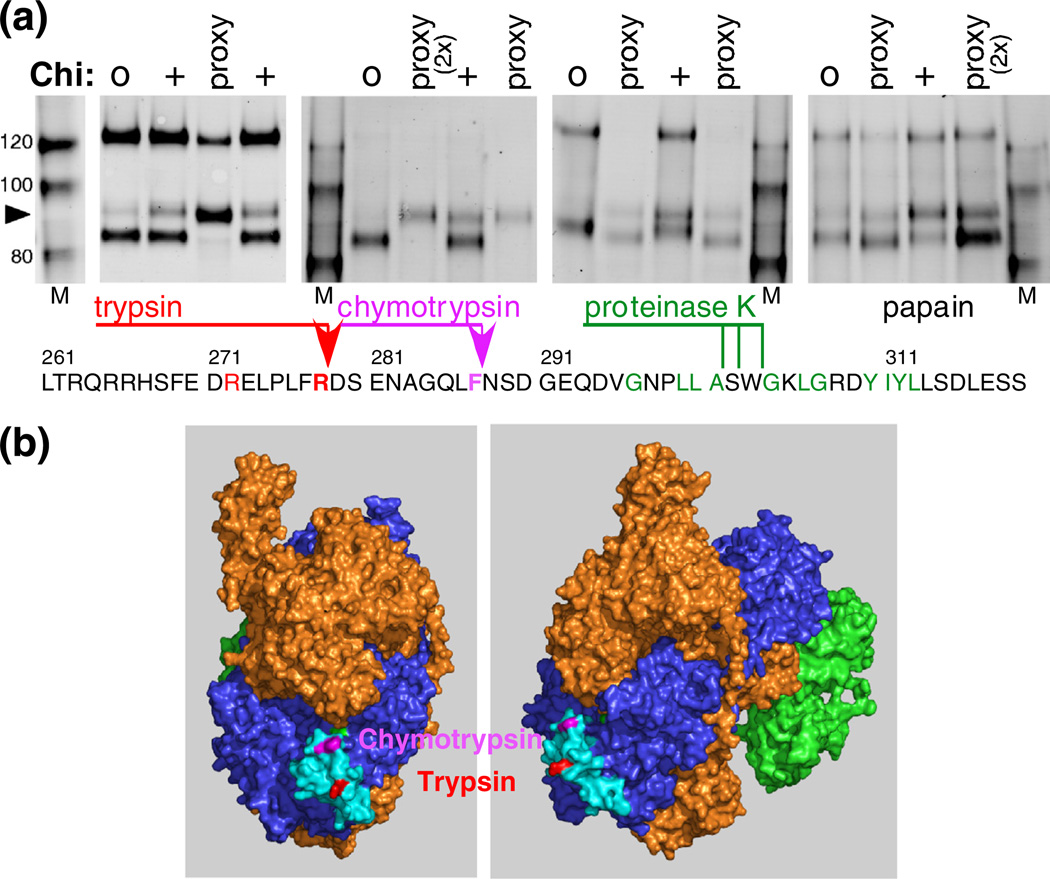
Fig. 5.
Location of Chi-dependent protease cleavages to a small exposed area of RecC. (a) RecBCD reacting with Chi0 or Chi+ DNA was treated with 32 nM trypsin, 100 nM chymotrypsin, 10 nM proteinase K, or 32 nM papain. RecBCD in buffer with DNA plus Mg2+ (proxy condition) was treated with the indicated protease (3 µM), and RecC was analyzed as in Fig. 2a. Sites of cleavage, determined by sequencing the trypsin- and chymotrypsin-derived Chi fragments (arrowheads), are shown on the RecC amino acid sequence. The location of the proteinase K cleavage was estimated by comigration with trypsin-cleaved substrate, using gels similar to those in Fig. 4. The substrate specificity of each protease includes the amino acids in color on the sequence. (b) The Chi-dependent sites of cleavage in the RecC polypeptide are in a disordered loop (cyan; residues 250–293) on the surface of the crystal structure [18]. The left view is rotated ~90° about the vertical axis relative to the right view.