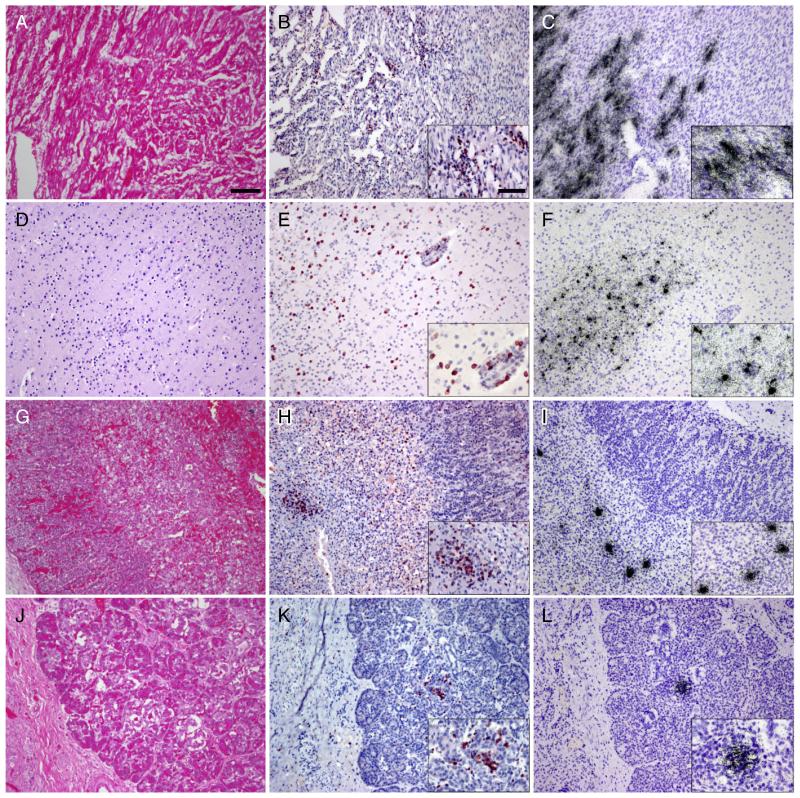
Fig. 1.
Histopathological analysis of autopsy tissues demonstrates widespread inflammation and infection. HE stains of the myocardium demonstrate severe edema and lymphocytic infiltration (A). Most infiltrating lymphocytes stain with an antibody to CD3 (B). In situ hybridization (ISH) for coxsackie B virus (CB4) (C) shows infection of cardiac myocytes in regions of inflammation. HE stains also demonstrate multifocal diffuse inflammation of brain parenchyma (D). Inflammatory cells in the brain predominantly stain with CD3 (E). ISH for CB4 (F) shows multifocal infection throughout the CNS. HE stain of the adrenal gland (G) (M = medulla, C = cortex) shows mild inflammatory infiltrate of the medulla more readily appreciated after immunostaining for CD3 (H). ISH for CB4 (I) shows infection limited to adrenal medulla. Inflammation is difficult to appreciate on HE stained sections of pancreas (J) but T cell infiltration is clear after immunostaining for CD3 (K). ISH for CB4 (L) shows infection of discrete islands of cells in regions of inflammation. All images at 10× magnification with insets at 20×, bar in 10× = 100 μm, in 20× = 50 μm.