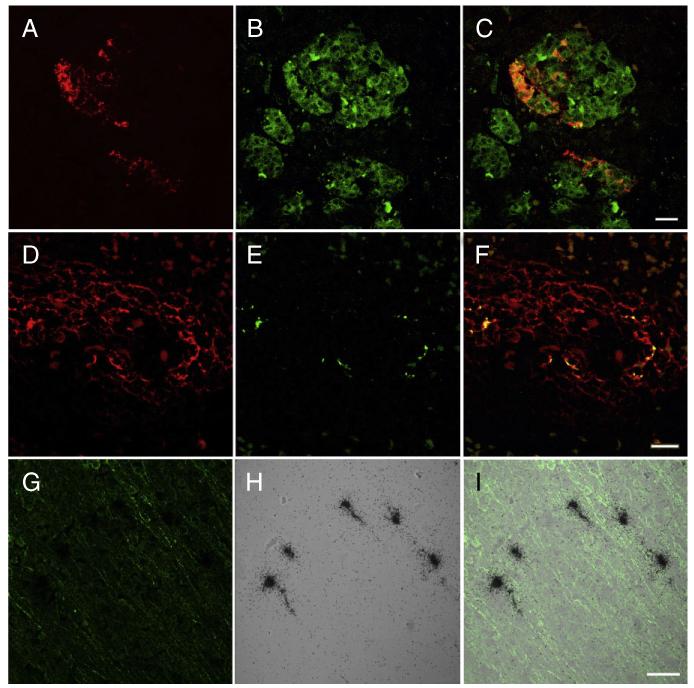
Fig. 3.
Double label immunocytochemistry for enterovirus (red) (A) and synaptophysin (green) (B) demonstrate infection of individual cells in the islets of Langerhans shown in the merged image (C). Double-label immunocytochemistry of spleen for CD21 (red) (D) and enterovirus (green) (E) demonstrated co-localization within follicles shown in the merged image (F). In situ hybridization with sense and anti-sense probes demonstrates that spleen signal was limited to detecting entrapped virion without detecting infected cells (see results). Double-label immunocytochemistry for microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) (green) (G) and in situ hybridization for coxsackie B virus (CB4) (black grains) (H) demonstrates infection of cortical neurons shown in the merged image (I).A–F bar = 20 μm, G–I bar = 50 μm.