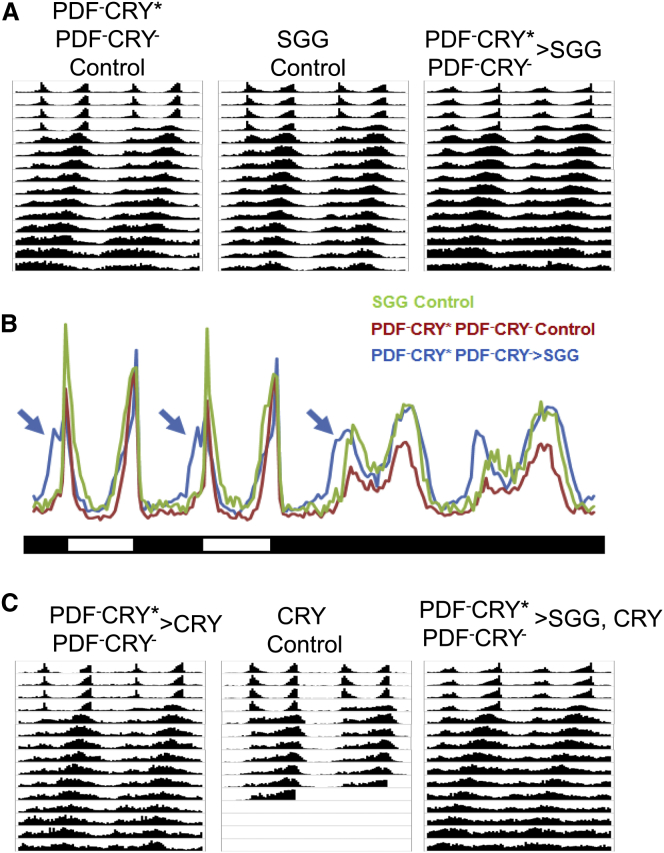
Figure 6.
Ectopic Expression of CRY Reveals a Functional Interaction with SGG
(A) Average locomotor activity profiles (4 days LD, 11 days DD) of PDF−CRY∗ ∩ PDF−CRY− > SGG flies and controls.
(B) Same data as in (A) but limited to the last 2 days of LD and first 2 days of DD. The profile for PDF−CRY∗ ∩ PDF−CRY− > SGG flies (blue) shows earlier anticipation of the dark-to-light transitions (blue arrows) compared to the other genotypes (PDF−CRY∗ ∩ PDF−CRY− Control, red and SGG Control, green).
(C) Average locomotor activity profiles (4 days LD, 11 days DD) of PDF−CRY∗ ∩ PDF−CRY− > CRY, CRY Control and PDF−CRY∗ ∩ PDF−CRY− > SGG, CRY flies. Only the latter genotype showed a shorter period of locomotor activity (see Table S5). Genotypes: PDF−CRY∗ ∩ PDF−CRY− > SGG, w, UAS-sgg; tim-GAL4/+; cry-GAL802e3m/ +; SGG Control, w, UAS-sgg; +/+; +/+; PDF−CRY∗ ∩ PDF−CRY− Control, w; tim-GAL4/+; cry-GAL802e3m/+; PDF−CRY∗ ∩ PDF−CRY− > CRY, w; tim-GAL4/+; cry-GAL802e3m/UAS-HAcry16.1; CRY Control, w; +/+; +/UAS-HAcry16.1; PDF−CRY∗ ∩ PDF−CRY− > SGG, CRY, w, UAS-sgg; tim-GAL4/+; cry-GAL802e3m/UAS-HAcry16.1. See also Table S5.