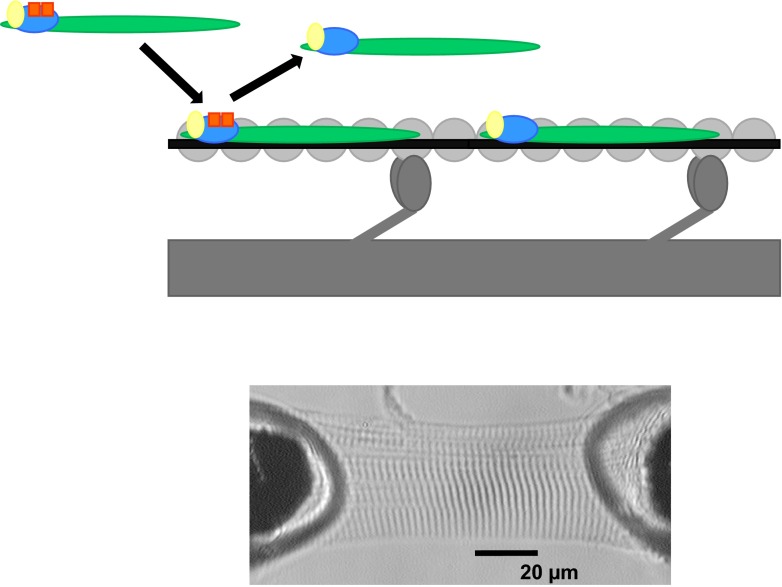
Fig. 1.
Schematic drawing of the thick and thin filaments exchanged with troponin complex. A schematic drawing of the thick and thin filaments, depicting exchange of endogenous troponin complex by exogenous troponin complex. The thick filament consists of myosin and myosin heads (dark grey) and the thin filament consists of actin monomers (light grey) spanned by tropomyosin (black) and the troponin complex: cTnC (yellow), cTnI (blue) and cTnT (green). In this drawing, exogenous cTnI is bisphosphorylated (orange squares), for example at Ser23/24. The endogenous unphosphorylated troponin complex is exchanged by exogenous phosphorylated troponin complex (arrows). To this end membrane-permeabilised cardiomyocytes were immersed with an exchange solution containing a high concentration of recombinant troponin complex. The lower image shows a single human cardiomyocyte in relaxing solution attached between a force transducer and a piezoelectric motor [this lower image has been published before: 18]