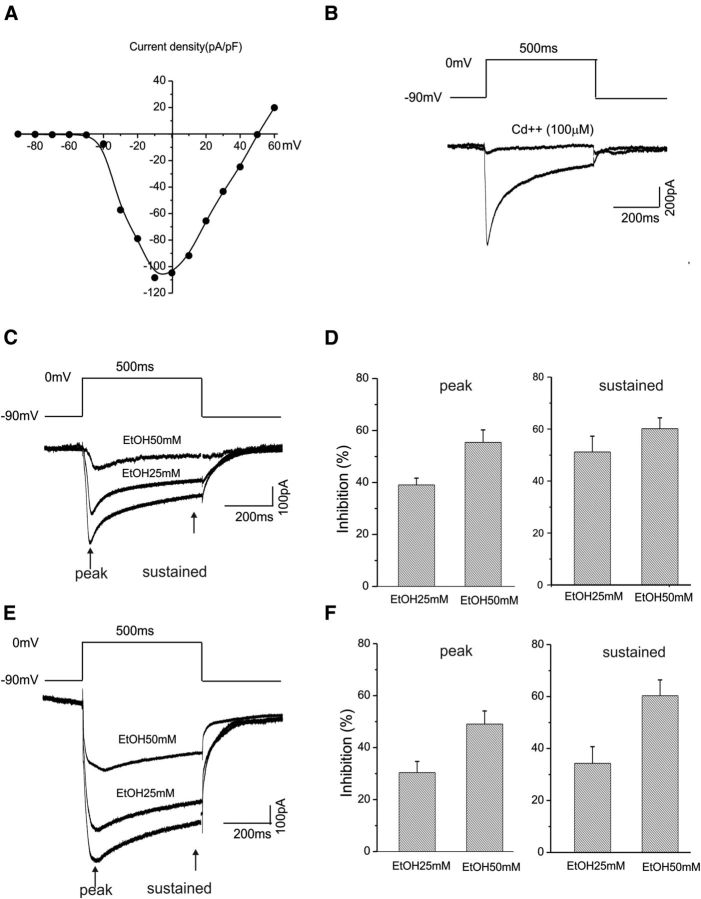
Figure 11.
EtOH inhibits whole-cell calcium currents recorded from CeA neurons. A, Voltage dependence of the total calcium current density in CeA neurons in which calcium ions are the charge carriers. Currents were elicited by 500 ms depolarizing test steps between −90 and 60 mV in 10 mV increments. B, The total calcium current can be completely abolished following bath application of the nonselective calcium channel blocker cadmium (100 μm). The voltage step for eliciting whole-cell calcium current is shown. C, Representative traces of calcium currents elicited by depolarizing neurons to 0 mV from −90 mV in response to bath application of 25 and 50 mm ethanol. The whole-cell total calcium currents were recorded using an internal solution containing calcium ions as charge carriers. D, Significant inhibitory effects of 25 mm (n = 5) and 50 mm (n = 11) ethanol on the total calcium currents are shown for both the peaks (left) and sustained components of total calcium currents (right). E, Representative whole-cell traces of barium currents elicited by depolarizing neurons to 0 mV from −90 mV in response to bath application of 25 and 50 mm ethanol. The whole-cell total currents were recorded using an internal solution containing barium ions as charge carriers. F, Significant inhibitory effects of 25 mm (n = 10) and 50 mm (n = 8) ethanol on the total calcium current are shown for the peaks measured at 20 ms (left graph) and 450 ms (right graph) following the start of the depolarizing step.