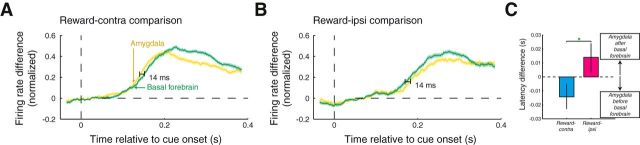
Figure 5.
Latency of reward information differs between the amygdala and BF. A, Reward-contra comparison as function of time relative to cue onset for amygdala sites (yellow) and BF sites (green). Firing rate differences were peak normalized and sign corrected before averaging over recording sites. The optimal time shift between the curves was determined using data within 50–400 ms after cue onset; an extended time window is plotted only for display purposes. B, Same as A for the reward-ipsi comparison. Here, the optimal time shift was determined using data within 90–440 ms after cue onset. Latency differences were significant in each case (p < 0.05). C, Latency differences for contralateral and ipsilateral reward information compared between the amygdala and BF. Error bars indicate the 95% confidence intervals of the latency differences. Green asterisk indicates the significance of the comparison (p < 0.05).