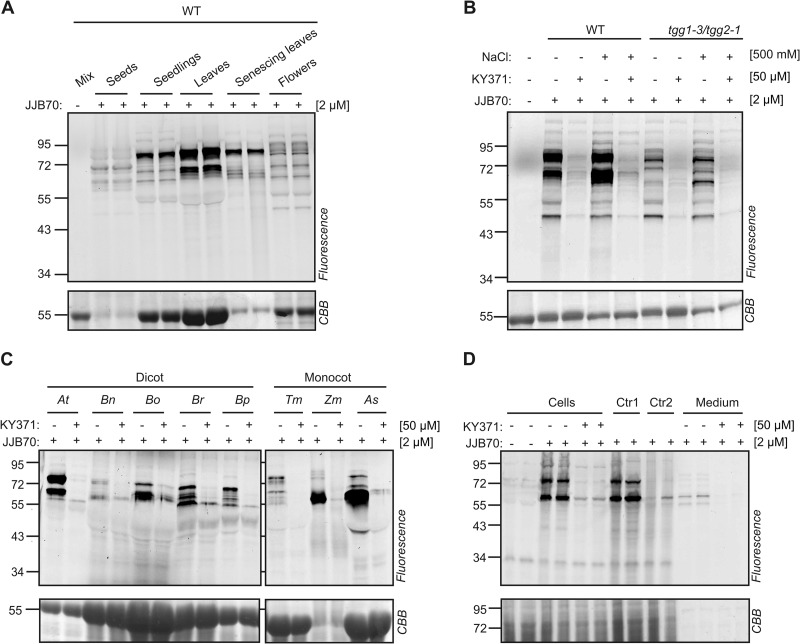
Fig. 5.
Glycosidase profiling is broadly applicable. A, Glycosidase activity profiles differ in different organs of wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana. Organ extracts containing ∼1.0–1.5 mg/ml soluble proteins were labeled with and without 2 μM JJB70 for 1 h. The different organ proteomes were mixed and used as a no-probe-control (mix). B, Flowers contain a diversity of active glycosidase in addition to TGG1 and TGG2. Flower proteins of WT and tgg1–3/tgg2–1 plants were extracted with and without 500 mM NaCl, pre-incubated with and without KY371 for 30 min and labeled with JJB70 at pH 6.0 C, Glycosidase profiling in different plant species. Leaf extracts of various dicot and monocot plants were pre-incubated with and without 50 μM KY371 for 30 minutes and incubated with 2 μM JJB70 for 1 h. The labeled proteins were detected by in-gel fluorescent scanning. At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Bn, Brassica napus; Bo, Brassica oleracea; Br, Brassica rapa; Bp, Brassica pekinensis; Tm, Triticum monococcum; Zm, Zea mays; As, Avena sativa. D, JJB70 labels glycosidases in living cells. Arabidopsis cell cultures were pre-incubated with and without 50 μM KY371 for 30 minutes and incubated with 2 μM JJB70 for 1 h. The cell cultures were ground with SDS-containing gel-loading buffer (GLB) to stop the labeling reaction. For control-1 (Ctr1), untreated cell cultures were ground with JJB70 for 30s, followed by adding GLB. For control-2 (Ctr2), untreated cell cultures were ground in GLB containing 2 μM JJB70. Liquid medium of cell cultures incubated with the probes was separated and concentrated using acetone precipitation.