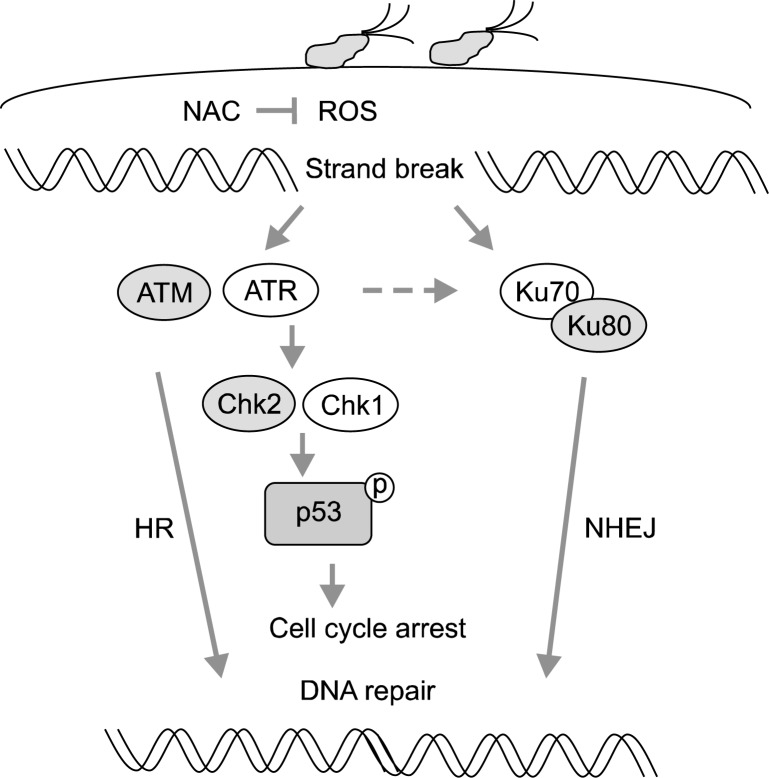
Fig. 2.
Proposed scheme of H. pylori-induced DDR. H. pylori infection increases oxidative stress in the infected tissue which triggers DDR by inducing DNA repair proteins (HR, NHEJ) and cell cycle regulators (Chk1, Chk2) and activate/induce p53. During DNA repair occurs, cell cycle is arrested and the damaged DNA may be repaired. On the other hand, the cells with the unrepaired DNA may proliferate, which may contribute to the development of cancer. DDR, DNA damage response; HR, homologous recombination; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining.