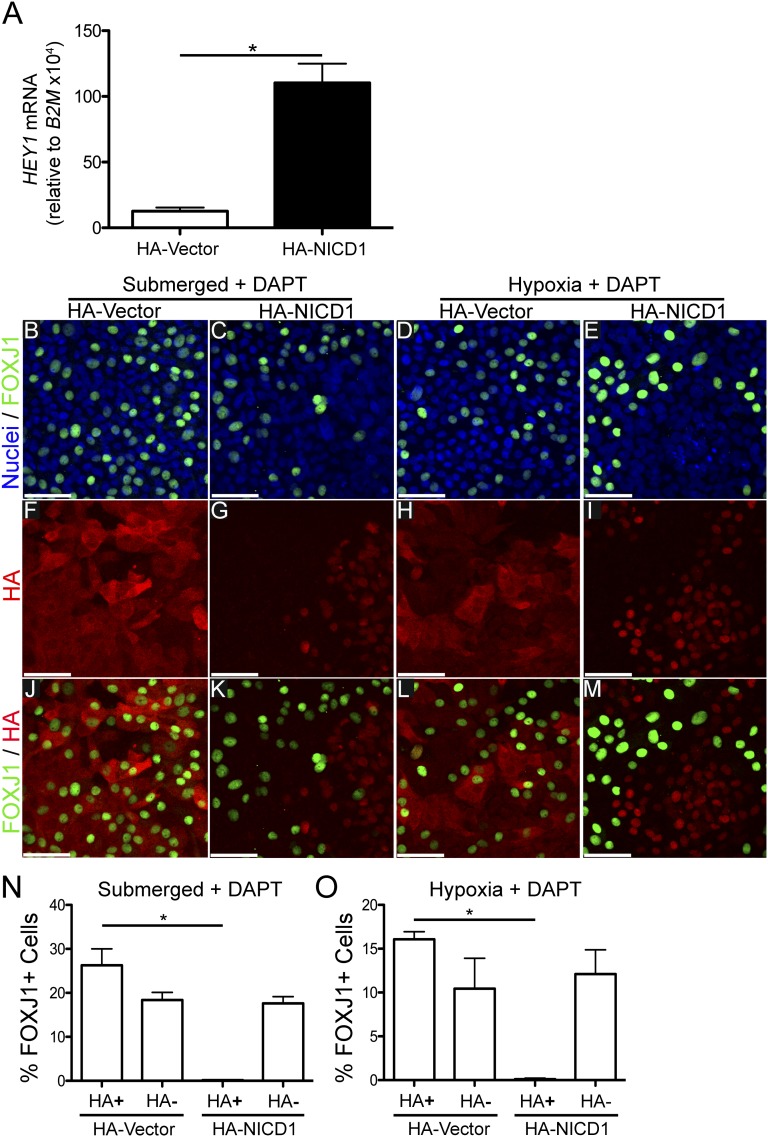
Figure 5.
Expression of influenza hemagglutinin epitope–tagged (HA)-NICD1 increases Notch signaling and inhibits FOXJ1 in DAPT-treated submerged and hypoxic cells. (A) qRT-PCR of HEY1 mRNA from NHBE cells transduced with lentiviruses expressing either HA-tagged NICD1 (HA-NICD1) or vector control (HA-vector), showing a significant increase in the Notch target gene, HEY1 mRNA, in HA-NICD1 transduced cells, indicating that HA-NICD1 induces Notch signaling. HEY1 mRNA was normalized to the housekeeping gene, B2M mRNA. Student’s t test (*P < 0.05; n = 3). (B–M) Representative extended-focus confocal immunofluorescent images of NHBE cells transduced with HA-NICD1 or HA-vector lentiviruses. Cells were grown for 3 weeks in submerged conditions with 10 μM DAPT or in hypoxia (0.5% O2) with 10 μM DAPT, and then stained for nuclei (Hoechst, blue), FOXJ1 (green), or HA (red). (B–E) Hoechst and FOXJ1 merged images, (F–I) images of HA alone, and (J–M) HA and FOXJ1 merged images. The images show cytoplasmic HA staining colocalizing with FOXJ1 in HA-vector transduced cells, whereas HA-NICD1 transduced cells have nuclear HA staining and significantly less colocalization with FOXJ1 staining. Quantification of percent FOXJ1+ HA-NICD1 or HA-vector transduced (HA+) and nontransduced (HA−) NHBE cells in submerged plus DAPT (N) and hypoxia plus DAPT (O) conditions showing significant reduction of FOXJ1+ cells in HA-NICD1 transduced cells compared with nontransduced cells, and to HA-vector control transduced cells in DAPT-treated submerged and hypoxic conditions. These results indicate that expression of HA-NICD1 inhibits ciliated cell differentiation in the presence of DAPT, and suggest that DAPT promotes ciliogenesis by blocking Notch signaling. A minimum of 500 cells from 3 different lung donors was counted for each group. Scale bar, 50 μm. Data shown are means (± SEM). One-way ANOVA (*P < 0.05; n = 3).