Figure 1.
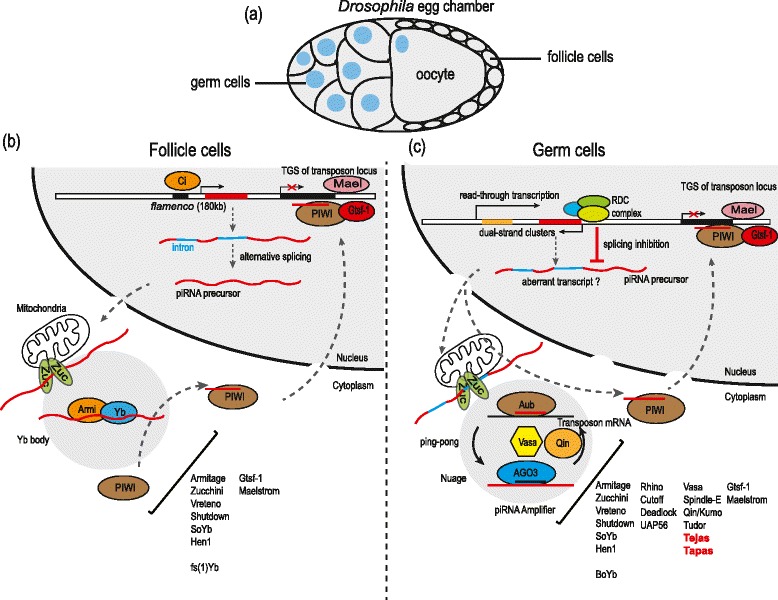
piRNA pathways in the Drosophila ovary. (a) A schematic representation of a fly egg chamber showing the germline (the single developing oocyte and 15 nurse cells) surrounded by a single layer of somatic follicle cells. (b) The unistrand piRNA cluster (piRNAs arising from only one strand) flamenco in the somatic follicle cells is transcribed by the transcription factor Ci. This approximately 180 kb long precursor is alternatively spliced and exported to the cytoplasm for processing in the nuage or Yb bodies. Nuage are perinuclear granules that contain most known piRNA biogenesis factors and are usually in the vicinity of mitochondria. Conversion of the long precursor RNA into approximately 24 nucleotide piRNAs takes place by an unknown mechanism called primary processing. Only PIWI that is loaded with piRNAs becomes licensed for import into the nucleus. Nuclear PIWI suppresses transposons via transcriptional gene silencing (TGS). A few nuclear factors (Gtsf-1 and Maelstrom) are known to be essential for TGS, but not for piRNA biogenesis. All known factors involved in the somatic pathway are listed. (c) The germline has both primary and secondary piRNA biogenesis pathways. Transcription of the dual-strand cluster (piRNAs arising from both strands) is thought to be non-canonical and arises from RNA polymerase II read-through from neighboring transcription units. A nuclear complex composed of Rhino-Deadlock-Cutoff (RDC) is essential for their transcription and is implicated in suppressing splicing and other RNA processing events [2]. Such ′aberrant′ transcripts are swept into the piRNA processing pathway. These are then processed in the cytoplasm to load all the three fly Piwi proteins. While many factors are shared with the follicle cells, a number of factors are unique to the germline compartment and they are required for the ‘ping-pong’ cycle, also known as secondary piRNA biogenesis. The RNA helicase Vasa orchestrates assembly of a piRNA Amplifier complex that generates new secondary piRNAs. Cytoplasmic Piwi proteins Aub and Ago3 destroy transposons by endonucleolytic cleavage, while PIWI acts in the nuclear compartment via TGS.
