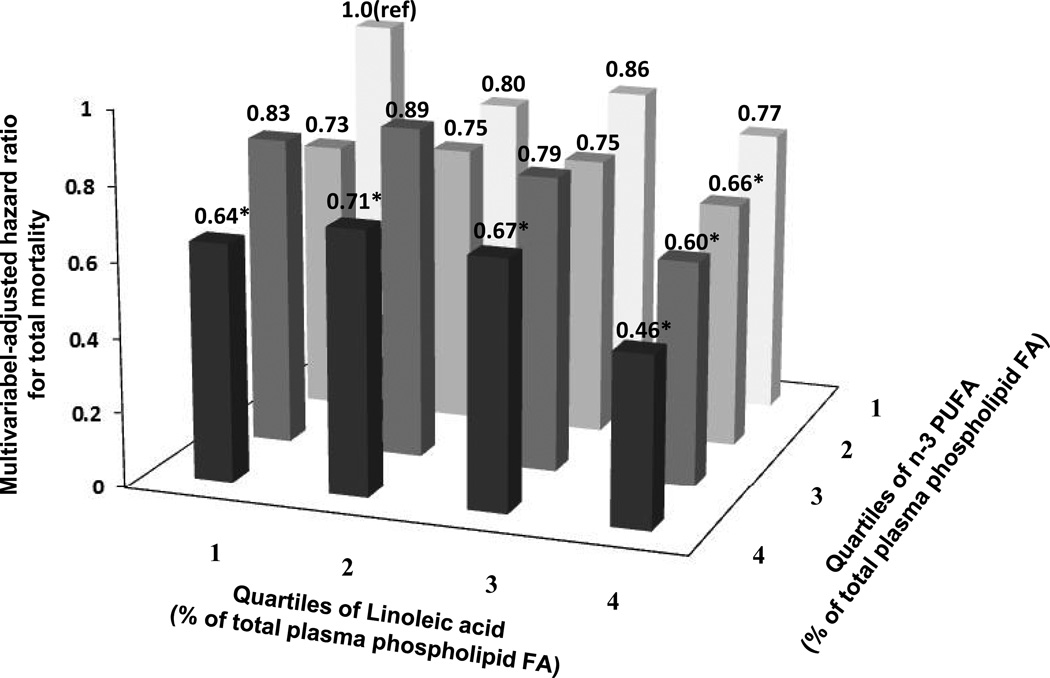
Figure 3.
Multivariable hazard ratios for total mortality by joint levels of plasma phospholipid linoleic acid and long-chain n-3 PUFA, adjusted for age, gender, race, enrollment site, education, smoking status, prevalent diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and hypertension, leisure-time physical activity, body mass index, waist circumference, and alcohol use, *P<0.05 compared with the referent category. Associations appeared independent, with little evidence for significant interaction between linoleic acid and long-chain n-3 PUFA (Wald test for multiplicative interaction: P=0.54).