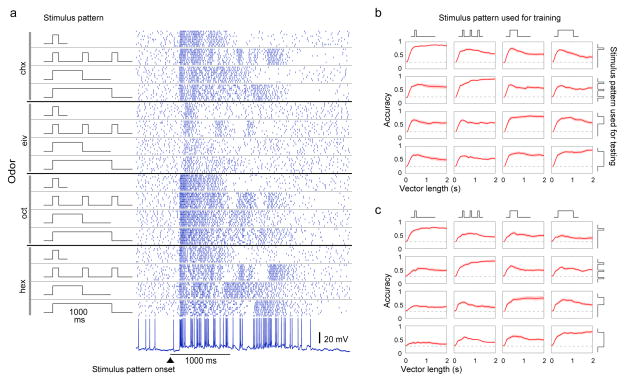
Figure 4.
Odor identity can be extracted from bLN responses even when odor stimulus pattern varies. (a) Rasterized spiking responses of a bLN to 4 odors, each presented in 4 different patterns (100 ms, 3×100 ms, 500 ms, and 1000 ms). (b) Classification accuracy (n = 11 bLNs) exceeded chance (dashed line = 0.25) even when the classifier was trained on responses to odors presented in one pattern and was tested on responses to the same odor set presented in another pattern. (c) Odor identity can be extracted from normalized bLN responses. The magnitude in each response vector (for each trial) was normalized by the total number of spikes occurring 2 s following the onset of odor. The classification accuracy, although less than that observed without normalization of response vectors in panel b, exceeds chance (0.25) in all cases. Shading shows s.e.m.