Fig. 2.
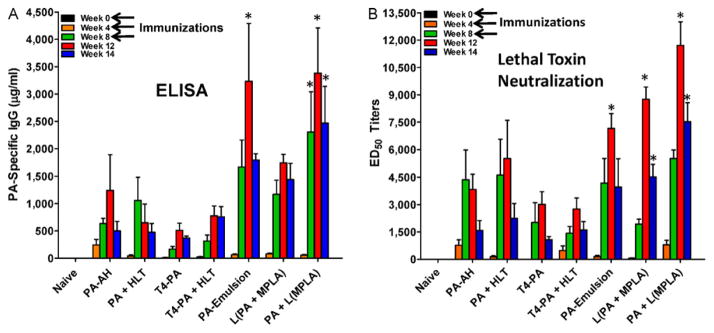
Immune responses to PA-adjuvant formulations in Rhesus macaques. (A) PA-specific IgG antibodies in sera of naive and immunized animals as determined by ELISA. Shown are the average concentrations of PA-specific IgG ± S.D. from each of the groups on weeks 0, 4, 8, 12, and 14, respectively. PA-emulsion induced significantly higher (p < 0.01) PA-specific IgG on week-12 compared to PA-AH. [PA + L(MPLA)] induced significantly higher PA-specific IgG on weeks 8 (p < 0.05), 12 (p < 0.001), and 14 (p < 0.01), respectively than PA-AH. (b) Lethal toxin neutralizing antibody titers (ED50 ) were determined in individual serum samples. At week 12, PA-emulsion immunized animals had significantly higher titers (p < 0.05) compared to PA-AH, while animals immunized with [L(PA + MPLA)] had significantly higher titers on weeks 12 (p < 0.001) and 14 (p < 0.05). The highest titers were induced in animals immunized with [PA + L(MPLA)] and ED50 titers were significantly higher than the titers induced by PA-AH at weeks 12 (p < 0.001) and 14 (p < 0.001).
