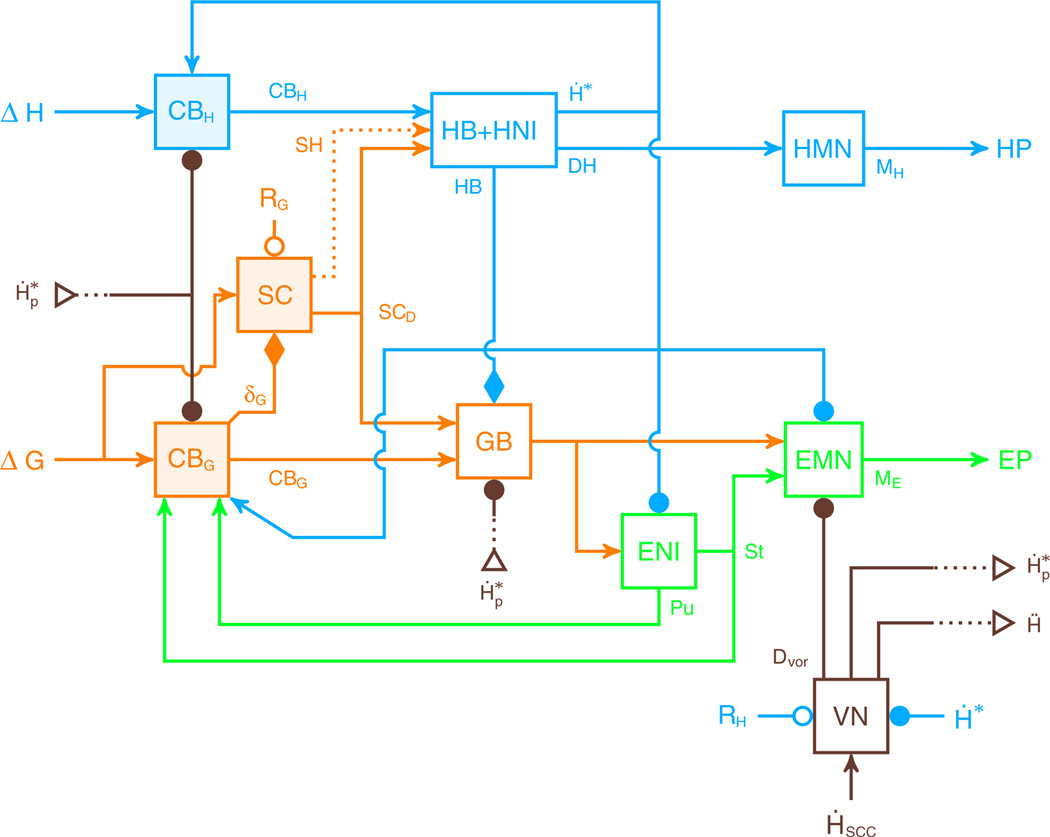
Fig. 2.
New model structure. The model includes three major pathways. Two receive the desired gaze displacement (ΔG) as input: one goes through the superior colliculus (SC) and projects to gaze- and head-related bursters, and one goes through one part of the cerebellum (CBG and orange items) and projects only to gaze-related neural areas. The third pathway (CBH and blue items) has the desired head displacement as input (ΔH); it goes through another part of the cerebellum and only projects to head-related neural areas (NRPC, NRG and HNI). The SC sends a collicular drive in the direction of the desired gaze displacement to both eye and head, but it does not control gaze trajectory. Additionally, the SC sends a collicular shunt to the head bursters (SH, orange dashed line). CBG is the core of the gaze controller; it sends a drive to eye-related neural areas to control gaze trajectory. It also sends a facilitation signal, δG, that mediates the collicular level of activity as a function of the gaze motor error (orange diamond). CBH controls head trajectory and sends a drive to the head-related neural areas. Brown items represent model elements related to head perturbations. Orange items represent parts of the model with a discharge related to gaze displacement. Blue items represent structures with a discharge related to head movements. Green items represent parts of the model with a discharge related to eye movements. In this figure, lines with arrowheads correspond to excitation, lines with filled circles correspond to inhibition, lines with filled diamonds correspond to facilitation, and lines with open circles correspond to reset signals. Open triangles represent cross-page connections. EP eye plant. HP head plant. GB gaze bursters. NRG nucleus reticularis gigantocellularis. NRPC nucleus reticularis pontis caudalis. HNI head neural integrator. ENI eye neural integrator. EMN eye motoneurons. HMN head motoneurons. VN vestibular nuclei. For other details see text