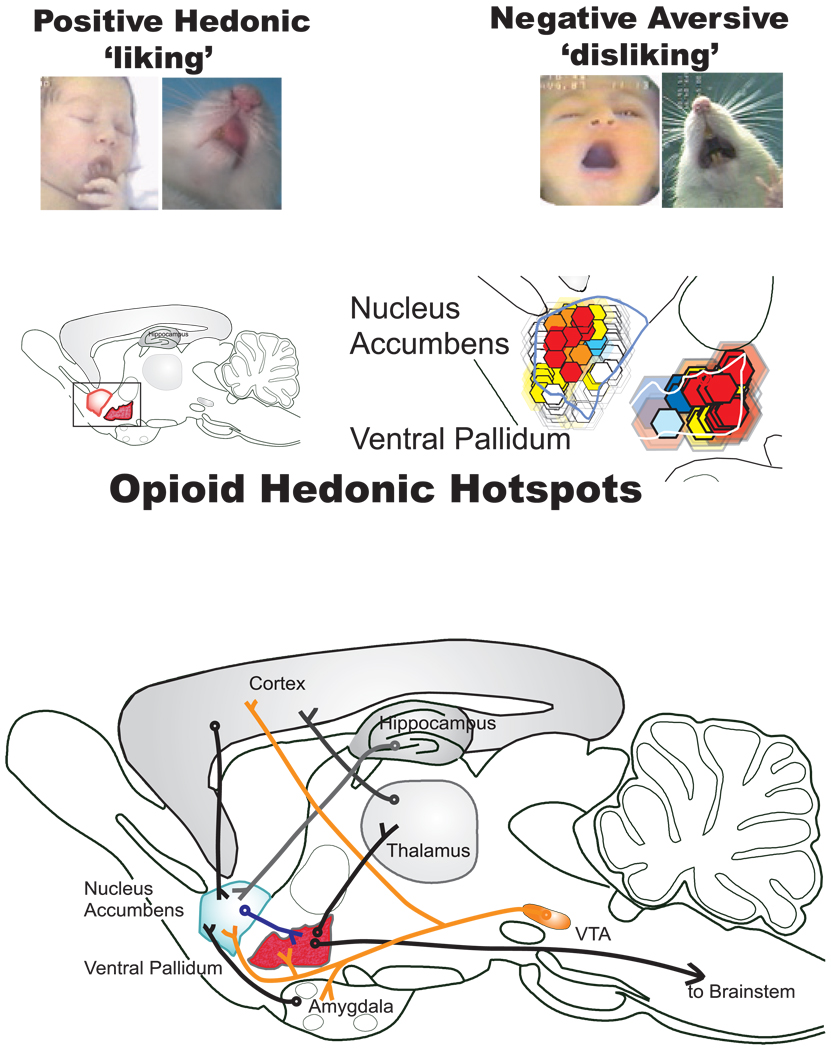
Fig. 24.1.
“Liking” reactions and brain hedonic hot spots. Top: Positive hedonic “liking” reactions are elicited by sucrose taste from human infant and adult rat (e.g., rhythmic tongue protrusion). By contrast, negative aversive “disliking” reactions are elicited by bitter quinine taste. Below: Forebrain hedonic hot spots in limbic structures where mu opioid activation causes a brighter pleasure gloss to be painted on sweet sensation. Red/yellow shows hot spots in nucleus accumbens and ventral pallidum where opioid microinjections caused the biggest increases in the number of sweet-elicited “liking” reactions. Based on Peciña and Berridge (2005), Smith and Berridge (2005), and Peciña, Smith, and Berridge (2006).