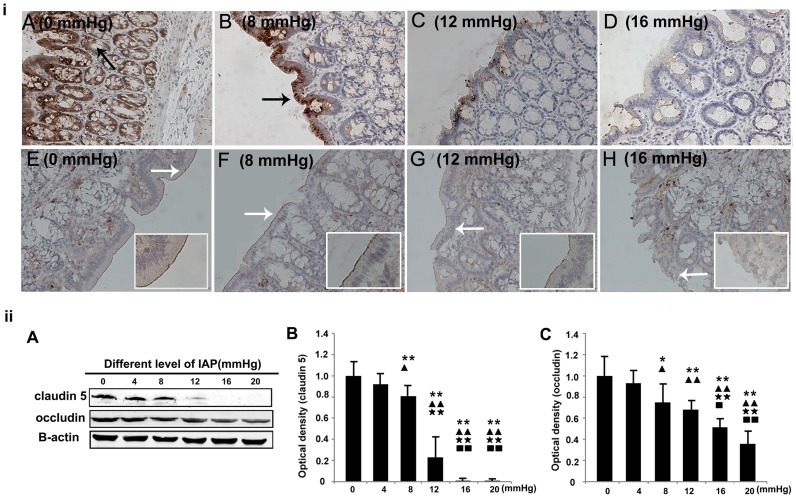
Figure 5. The effects of different grades of nitrogen pneumoperitoneum on the expression levels of TJ proteins.
i: Immunohistochemical localization of claudin 5 and occludin (×200). Increased intra-abdominal pressures tended to reduce the expression levels of claudin 5 and occludin. A–D: Claudin 5. The black arrow indicates the positive signals for claudin 5 in the lateral membrane of the epithelia. E–H: Occludin. The white arrows indicate the positive signals for occludin in the apical cell borders of the colonic epithelia. ii: Western blotting results for claudin 5 and occludin. The expression levels of the proteins were normalized relative to actin. Compared with the 0-mmHg group, the 8-, 12-, 16-, and 20-mmHg groups had significantly reduced densities of claudin 5 and occludin. All data are shown as means ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, vs. 0 mmHg; ▴P<0.05, ▴▴P<0.01, vs. 4 mmHg;★★P<0.01, vs. 8 mmHg; ▪P<0.05, ▪▪P<0.01, vs. 12 mmHg.