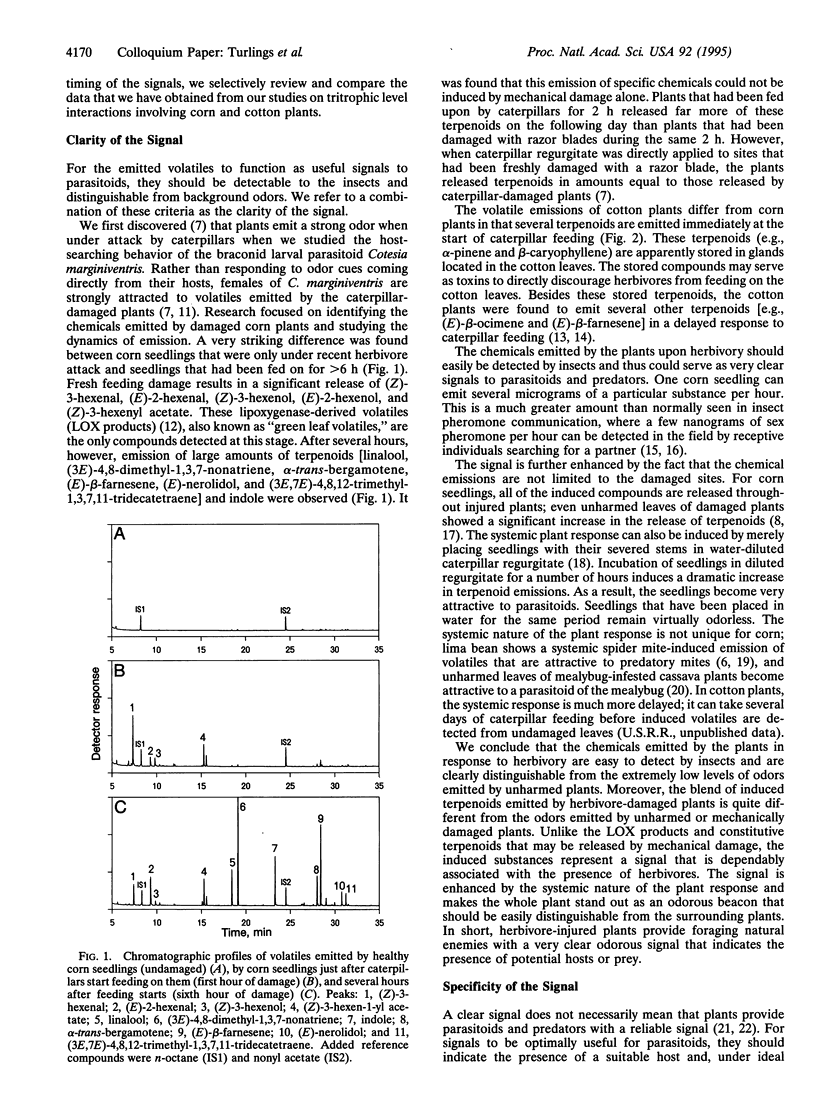
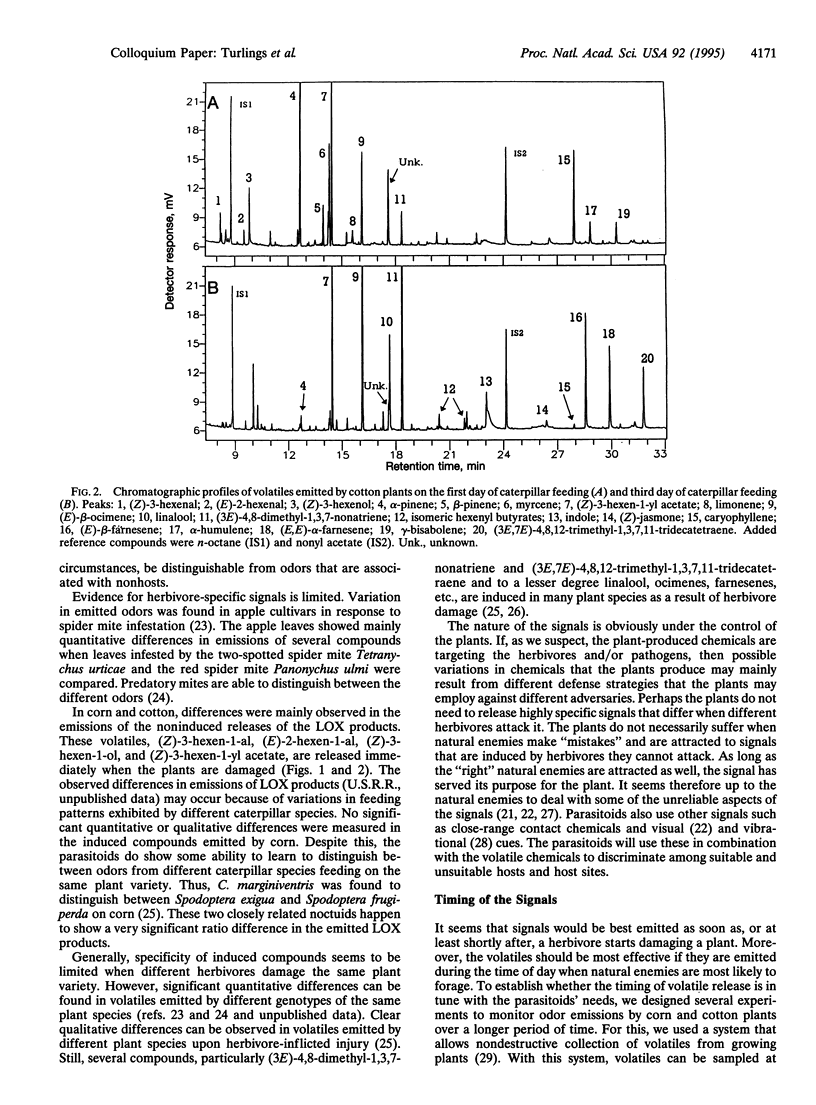
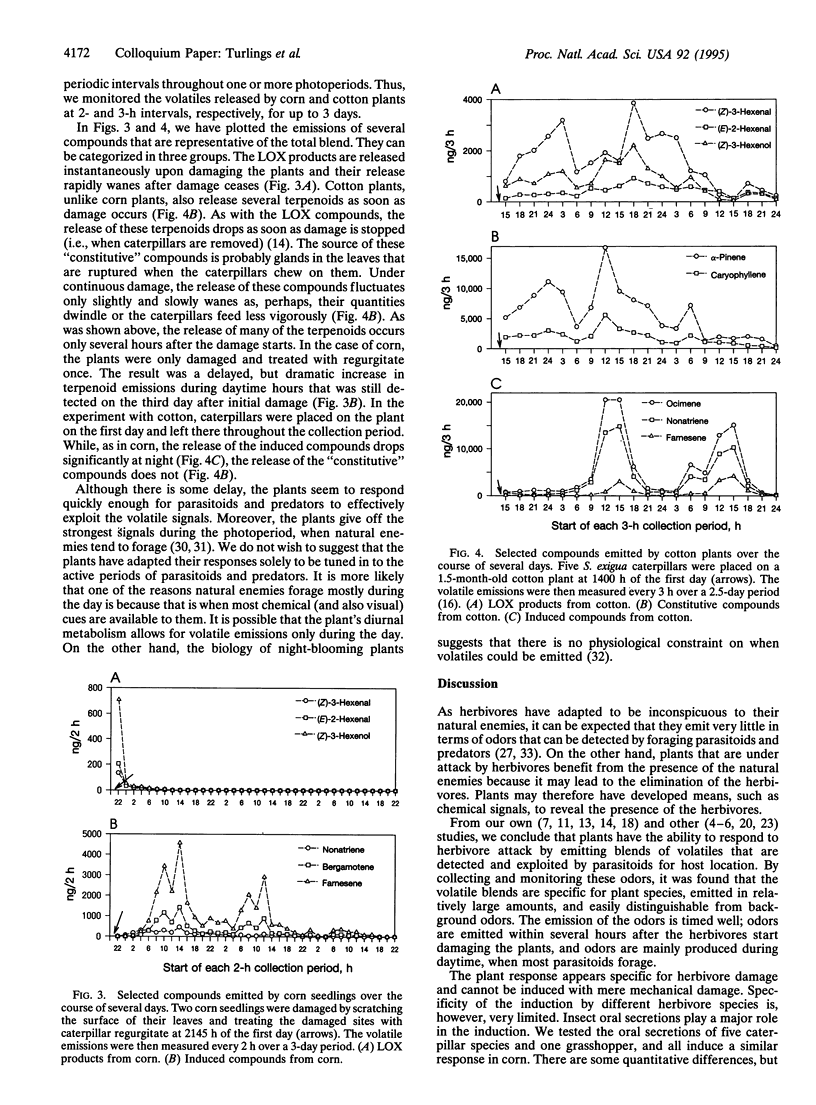
Abstract
Parasitic and predatory arthropods often prevent plants from being severely damaged by killing herbivores as they feed on the plants. Recent studies show that a variety of plants, when injured by herbivores, emit chemical signals that guide natural enemies to the herbivores. It is unlikely that herbivore-damaged plants initiate the production of chemicals solely to attract parasitoids and predators. The signaling role probably evolved secondarily from plant responses that produce toxins and deterrents against herbivores and antibiotics against pathogens. To effectively function as signals for natural enemies, the emitted volatiles should be clearly distinguishable from background odors, specific for prey or host species that feed on the plant, and emitted at times when the natural enemies forage. Our studies on the phenomena of herbivore-induced emissions of volatiles in corn and cotton plants and studies conducted by others indicate that (i) the clarity of the volatile signals is high, as they are unique for herbivore damage, produced in relatively large amounts, and easily distinguishable from background odors; (ii) specificity is limited when different herbivores feed on the same plant species but high as far as odors emitted by different plant species and genotypes are concerned; (iii) the signals are timed so that they are mainly released during the daytime, when natural enemies tend to forage, and they wane slowly after herbivory stops.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Law J. H., Regnier F. E. Pheromones. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:533–548. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loughrin J. H., Manukian A., Heath R. R., Turlings T. C., Tumlinson J. H. Diurnal cycle of emission of induced volatile terpenoids by herbivore-injured cotton plant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):11836–11840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.11836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turlings T. C., Tumlinson J. H., Lewis W. J. Exploitation of herbivore-induced plant odors by host-seeking parasitic wasps. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1251–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4985.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turlings T. C., Tumlinson J. H. Systemic release of chemical signals by herbivore-injured corn. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8399–8402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


