Figure 4.
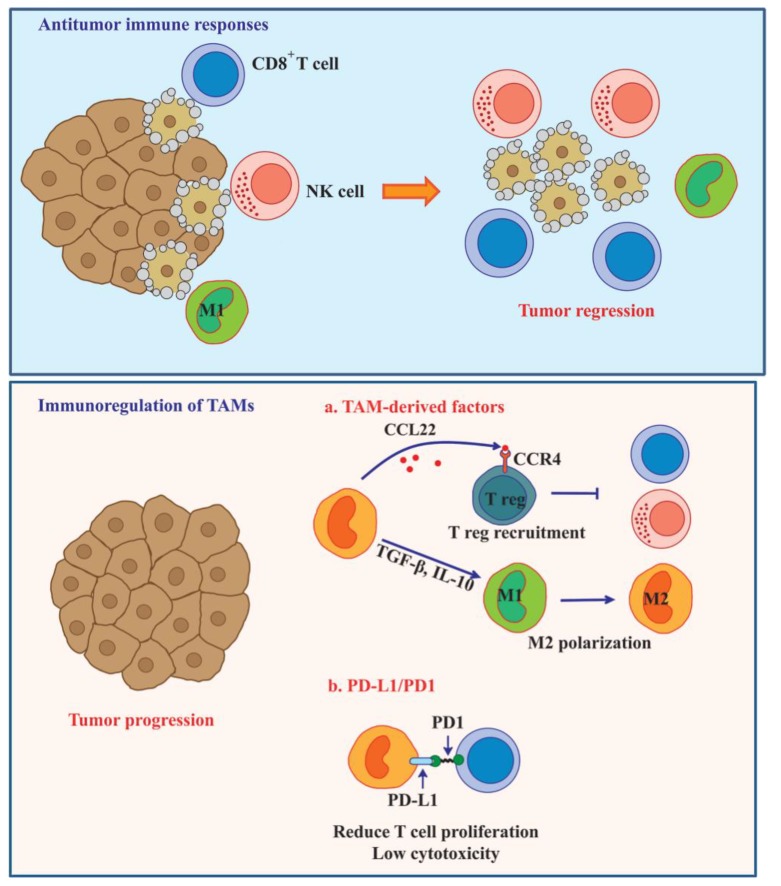
TAMs induce immune dysfunction and enhance tumor progression. Immune system promotes the elimination of tumor by the function of CD8+ T cell, NK cell, and M1 macrophage. These immune responses are modulated or suppressed by the tumor microenvironment to allow tumor cells survival. The inefficacy of immune cells to destroy tumor is regulated by TAMs. TAMs support the immunosuppression in tumor by secreting several factors such as CCL22, IL-10, and TGF-β. Treg recruitment into tumor is controlled by the CCL22/CCR4 axis. These cells suppress immune surveillance through multiple mechanisms including inhibition of T cell proliferation and activation or inhibition of NK cell cytotoxicity. Releasing of immunosuppressive factors such as IL-10 and TGF-β can also polarize M1 to M2 macrophage. TAMs also directly inhibit T cell proliferation and cytotoxicity by the PD-L1/PD1 signaling axis.