Figure 1.
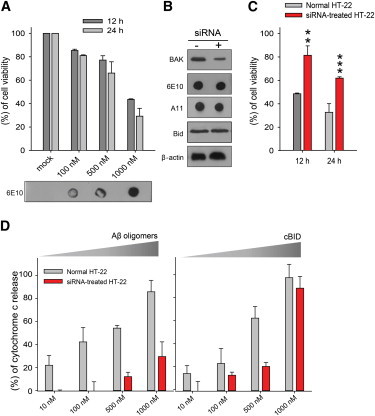
Aβ oligomer-induced cell death and cytochrome c release from siRNA-transfected and normal HT-22 cells. (A) Cell viability of HT-22 cells was evaluated with the MTT assay, 12 h and 24 h, after treatment of the indicated concentrations of Aβ oligomers. Transfected Aβ oligomers were confirmed with Dot blot using anti-β amyloid (6E10) antibody. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. (B) Immunoblot analysis of BAK and Aβ oligomers protein in HT-22 cells using anti-BAK and anti-β amyloid (6E10) antibody. HT-22 cells were pretreated with/without the 20 nM BAK siRNA for18 h. A quantity of 1000 nM Aβ oligomers were treated with protein transfection regents. Anti-β-actin and anti-Bid antibodies used as control is shown. (C) Aβ oligomer-induced cell death was compared in normal and BAK KD HT-22 cells using the MTT assay. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (∗∗∗P < 0.005; ∗∗P < 0.01 compared with Aβ oligomers-treated (1 μM) normal HT-22 cells pretreated with vehicle). (D) Measurement of cytochrome c release from isolated mitochondria of HT-22 cells using a colorimetric ELISA assay kit (Invitrogen). The data represent the mean ± SD of four independent experiments. Concentrations are given in moles of monomeric Aβ. To see this figure in color, go online.
