Figure 1.
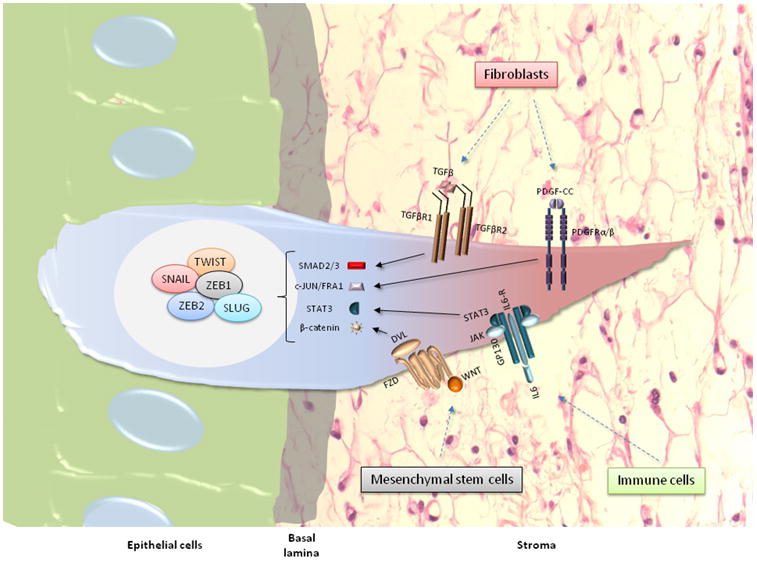
Connecting extracellular signals to EMT transcription factors. Contextual signals, such as TGF-β, WNT proteins, platelet-derived growth factors (PDGFs) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), arising from autocrine or paracrine signaling networks can activate intracellular signaling factors that influence the activation or maintenance of the EMT transcription factor network during an EMT. TGF-βR1 and TGF-βR2 are two TGF-β receptors; PDGF-CC is a specific member of the PDGF family; PDGFR-α/β indicates two distinct receptor serine/threonine kinases; STAT3 is signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; IL-6R is the IL-6 receptor; gp130 is a membrane glycoprotein; SMAD2/3 indicates SMAD2 and SMAD3; c-JUN/FRA1 are heterodimeric subunits of the AP-1 complex (please note that AP-1 has been defined earlier in Box 1); NK cells are natural killer cells.
