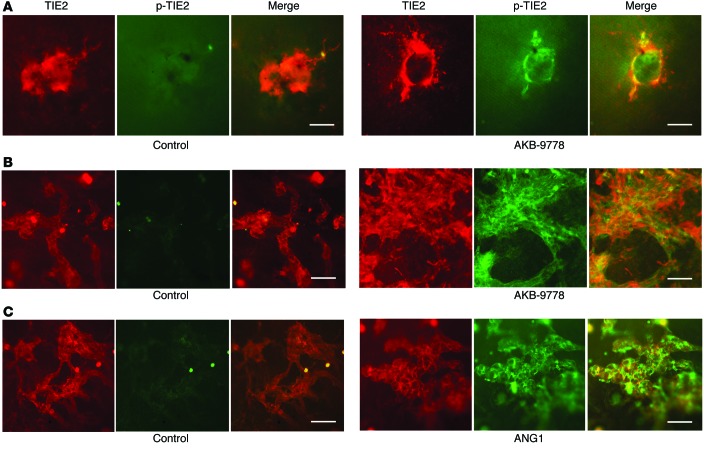
Figure 4. AKB-9778 stimulates TIE2 phosphorylation in subretinal and retinal NV.
(A) At P21, Rho-VEGF–transgenic mice were given a s.c. injection of vehicle or 20 mg/kg AKB-9778, and after 12 hours, retinal flat mounts were immunohistochemically stained for TIE2 (red) and p-TIE2 (green). In vehicle control mice, new vessels stained for TIE2, but not p-TIE2, while in AKB-9778–treated mice, they stained for both TIE2 and p-TIE2. Scale bars: 100 μm. (B) At P16, mice with ischemic retinopathy were administered a s.c. injection of vehicle or 20 mg/kg AKB-9778 or an intraocular injection of 500 ng ANG1, and after 12 hours, retinas were double labeled for TIE2 (red) and p-TIE2 (green). Eyes of vehicle control mice showed extensive TIE2+ NV on the retinal surface that did not stain for p-TIE2, but in AKB-9778–treated mice, the TIE2+ NV also stained for p-TIE2. Scale bars: 100 μm. (C) Likewise, ischemia-induced retinal NV stained for both TIE2 and p-TIE2 after intraocular injection of 500 ng ANG1. Scale bars: 100 μm.