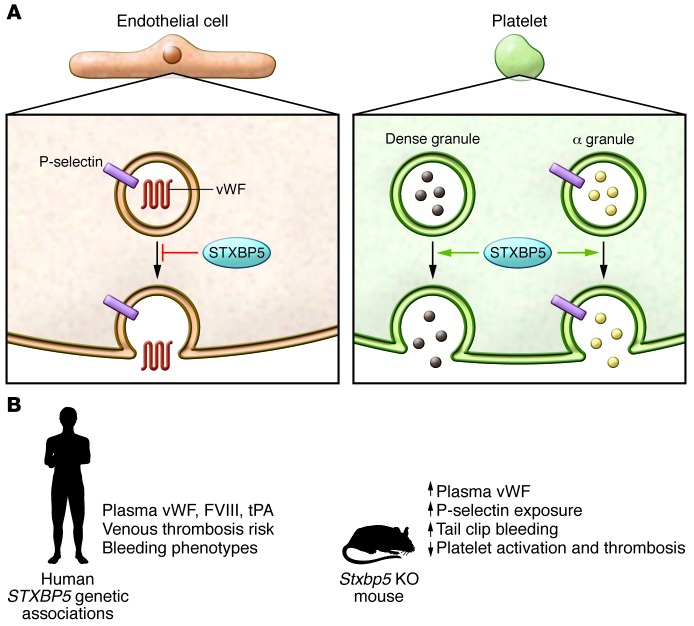
Figure 1. STXBP5 differentially influences exocytosis in platelets and endothelial cells.
(A) STXBP5 inhibits regulated exocytosis from endothelial cells, but promotes granule secretion from platelets. In both cell types, STXBP5 interacts with components of the SNARE machinery, but the details of these interactions appear distinct. In endothelial cells, there is no colocalization with WPBs, and the number, size, and morphology of these organelles is not influenced by STXBP5. In platelets, there is no colocalization of STXBP5 with α, dense, and lysosomal granules, but the granule cargo composition is altered. (B) Genetic associations and effects of STXBP5 deficiency. In humans, STXBP5 has consistently been identified in GWAS to be associated with the regulation the plasma levels of several coagulation factors, with bleeding, and with the risk of venous thrombosis. Stxbp5 KO mice exhibit a spectrum of hemostatic phenotypes that are consistent with the role of STXBP5 function in endothelial cells and platelets. FVIII, factor VIII; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator.