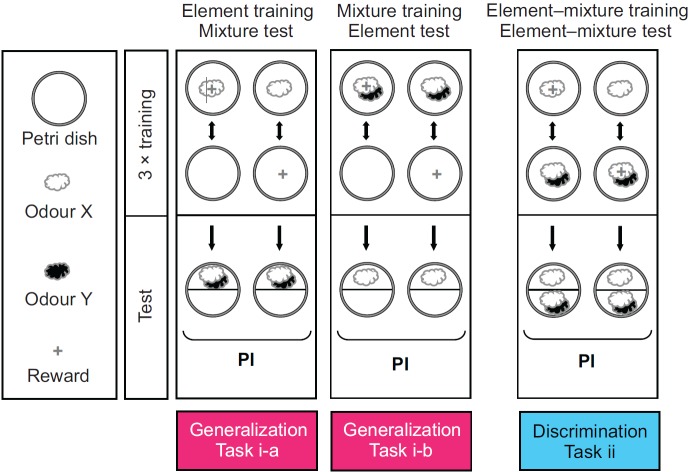
Fig. 1.
General procedures of the generalization and discrimination tasks. Task i is a generalization task. In Task i-a, larvae are trained to associate an odour X (open cloud) with a sugar reward, and are subsequently tested for their approach to a binary mixture containing the trained odour (XY; open and filled clouds); reciprocal groups are tested in the same way, yet after unpaired presentations of odour and reward. From the difference in preference between these two kinds of experimental group, the associative performance index (PI) is calculated. The same two-group design is used for Task i-b, except that animals are trained to associate a binary mixture with a sugar reward and are tested for their approach to one of its constituent elements. Task ii is a discrimination task, such that larvae are both trained and tested differentially between an odour versus a binary mixture containing it. The following odours were used, in all possible combinations, as X and Y (see Table 1 and Materials and methods for details): 1-octanol (1O), n-amyl acetate (AM), 3-octanol (3O), benzaldehyde (BA) and hexyl acetate (HA).