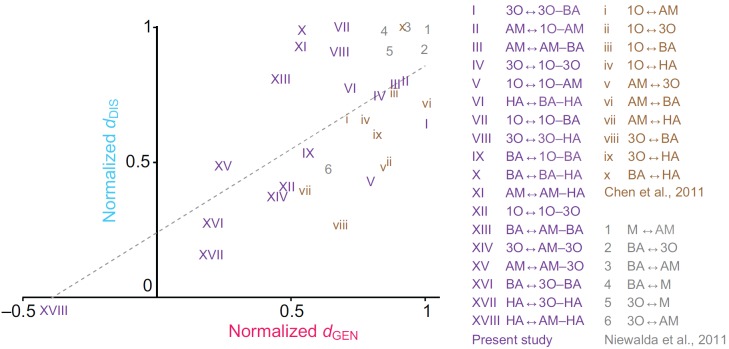
Fig. 5.
Correlation of normalized perceptual distance scores from this study and the literature. Normalized perceptual distances correlate between generalization and discrimination tasks not only for the present study (I–XVIII, purple), but also for previously published ones probing for element–element perceptual distances using a larval odour–sugar learning paradigm [i–x, brown (Chen et al., 2011)] and for element–element distances using odour–shock learning in adult Drosophila [1–6, grey (Niewalda et al., 2011)]. The plot presents normalized dDIS scores on the y-axis and normalized dGEN scores on the x-axis (Spearman's rank correlation: rS=0.53, P<0.05, N=34) (the stimulus combinations and odours used in the respective studies are listed in the keys). Thus, across all three studies, distances scores approximated from generalization and discrimination tasks were concordant. M, 4-methylcyclohexanol. See Fig. 1 legend for other odour definitions.