Figure 1.
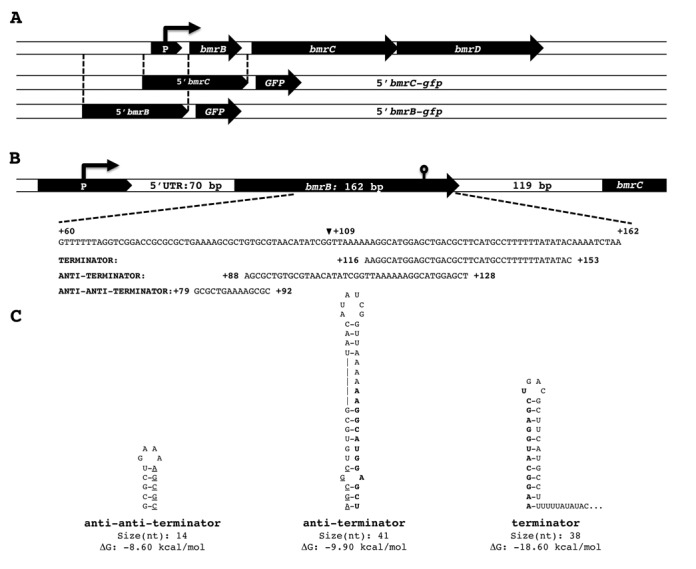
Genomic context of the bmrCD locus and transcriptional GFP fusions. A. The top line depicts the genomic context of the ABC transporter genes bmrC and bmrD, which are preceded by the small open reading frame bmrB. The two lines below represent the relative positions of the two regions selected for construction of the transcriptional 5′bmrC-gfp and 5′bmrB-gfp fusions. B. Detailed representation of the regulatory region upstream of bmrC, including the segment of bmrB (nucleotides 60–162) in which predicted terminator, anti-terminator and anti-anti-terminator structures are encoded. These three putative structures are assigned with their nucleotide positions relative to the first nucleotide of bmrB. The black arrowhead marks nucleotide 109 after which bmrB was truncated in pRM3-bmrB109. In addition, the 5′UTR upstream of bmrB and the intergenic region between bmrB and bmrC are indicated. C. Structures of the putative anti-anti-terminator, anti-terminator and terminator, with their respective sizes and Gibbs free energy (ΔG) values, as predicted by RibEx: Riboswitch Explorer. The overlap in the terminator and anti-terminator structures is marked in bold, and the overlap in the anti-terminator and anti-anti-terminator structures is marked by underlining.
