Figure 5.
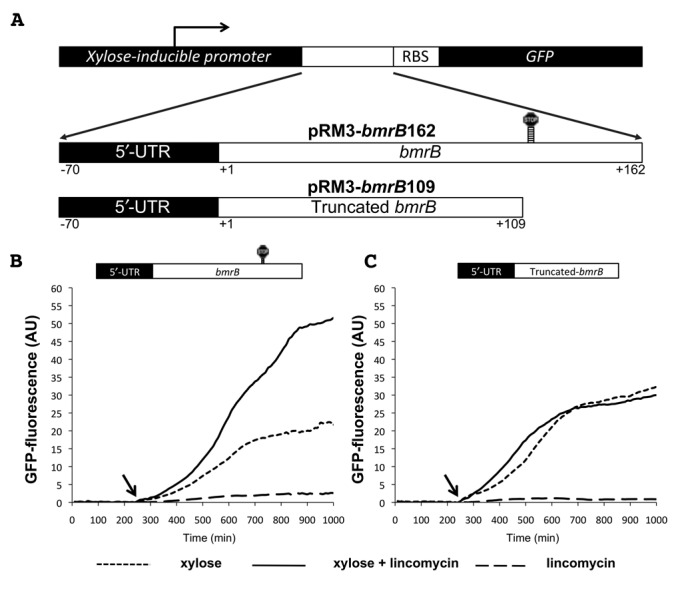
The 3′ end of bmrB is required for lincomycin-induced bmrCD transcription. A. Schematic representation of a part of plasmids pRM3-bmrB162 and pRM3-bmrB109. pRM3-bmrB162 was constructed by fusing the complete sequence of bmrB and its 5′-UTR to the gfp gene. pRM3-bmrB109 was constructed by fusing a truncated version of bmrB, consisting of this gene's first 109 nucleotides to gfp. Accordingly, pRM3-bmrB109 lacks the predicted terminator within bmrB and part of the predicted anti-terminator. Panels B and C show the GFP fluorescence of B. subtilis carrying pRM3-bmrB162 (B) or pRM3-bmrB109 (C) in response to xylose, lincomycin (0.75 μg/ml), or a combination of xylose and lincomycin added at the time points indicated by arrows. Xylose-induced GFP fluorescence, given in AU, was used as measure for the level of gfp expression.
