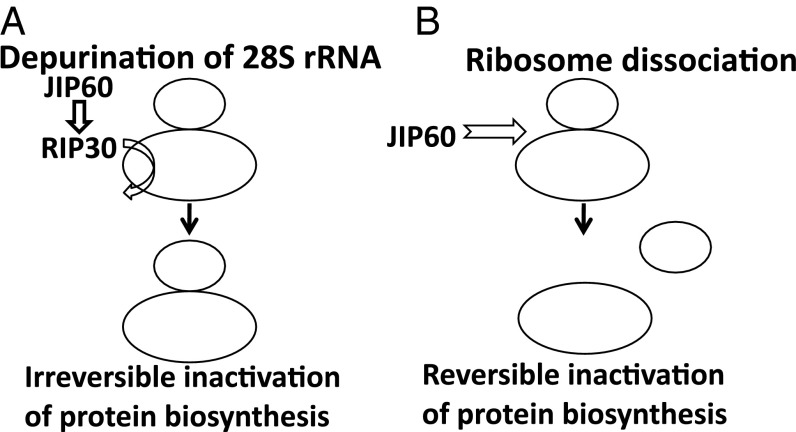
Fig. 1.
Models of the action of JIP60 and its RIP30 domain. (A) After processing of JIP60, the released RIP30 is considered to act as N-glycosidase and to catalytically remove a conserved adenine residue in the α-sarcin/ricin loop of 28S rRNA, leading to an irreversible arrest of translational elongation in the cytosol. (B) JIP60 itself and without further processing is thought to bind to 80S ribosomes and cleave them into their 60S and 40S ribosomal subunits. This effect is dose-dependent and would lead to a reversible block in protein synthesis.