Figure 3. Transcription rate.
(A) Normalized transcription rate  (Equation 12) for a σ
70-dependent promoter as a function of the number of alternative sigma factors. The numbers of
(Equation 12) for a σ
70-dependent promoter as a function of the number of alternative sigma factors. The numbers of  and cores are fixed. The blue line is for a saturated promoter (with
and cores are fixed. The blue line is for a saturated promoter (with  M) and the cyan line for an unsaturated promoter (with
M) and the cyan line for an unsaturated promoter (with 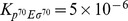 M). (B) Comparison of model predictions (lines) with an in vitro competition experiment [29] with a fixed amount of core and σH and different amounts of
M). (B) Comparison of model predictions (lines) with an in vitro competition experiment [29] with a fixed amount of core and σH and different amounts of  (stars). The plot shows the transcription rate of a σH-dependent gene (normalized to the maximal value) as a function of the concentration
(stars). The plot shows the transcription rate of a σH-dependent gene (normalized to the maximal value) as a function of the concentration 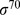 . (C) The sigma-core and the holoenzyme-promoter dissociation constants (see Table 2) are determined by fitting the results of transcription rate experiments with a fixed amount of cores in the same conditions as in (B) without competition in the presence of a DNA template containing σH- and σ
70-driven genes [29], [32]. (D) When a σ
70-dependent promoter also binds another type of holoenzyme or overlaps to another promoter,
. (C) The sigma-core and the holoenzyme-promoter dissociation constants (see Table 2) are determined by fitting the results of transcription rate experiments with a fixed amount of cores in the same conditions as in (B) without competition in the presence of a DNA template containing σH- and σ
70-driven genes [29], [32]. (D) When a σ
70-dependent promoter also binds another type of holoenzyme or overlaps to another promoter, 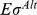 also acts as a repressor of the σ
70-dependent transcription. (E) Normalized transcription rate of a saturated and unsaturated σ
70-dependent promoter as a function of the number of
also acts as a repressor of the σ
70-dependent transcription. (E) Normalized transcription rate of a saturated and unsaturated σ
70-dependent promoter as a function of the number of 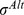 (blue and cyan solid lines with
(blue and cyan solid lines with 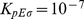 M and
M and  M, respectively). The dashed line show the corresponding results in the absence of repression by promoter sharing or overlapping.
M, respectively). The dashed line show the corresponding results in the absence of repression by promoter sharing or overlapping.

