Figure 5.
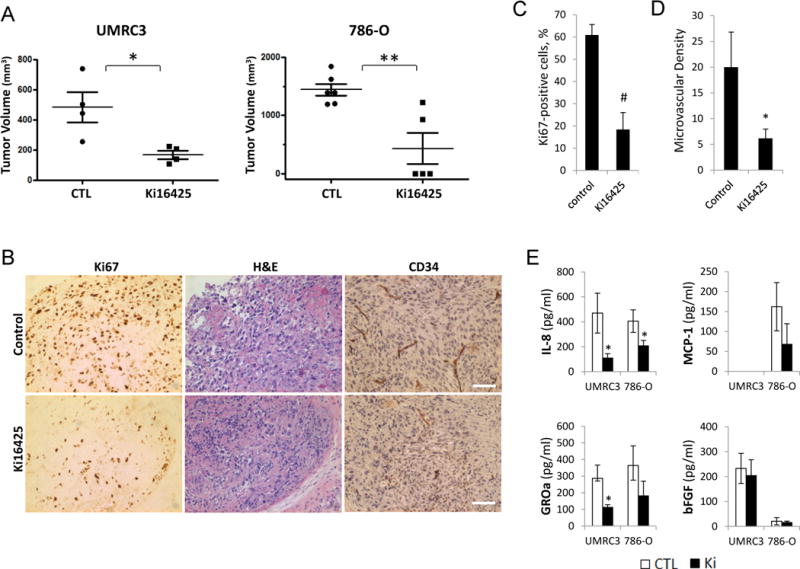
Effects of Ki16425 on tumor growth and angiogenesis in mouse models of RCC. A, BALB/c nude mice were given s.c. injections of RCC cells (UMRC3 and 786-O) in the right flank, randomized into two groups, and administered either PBS (control, CTL) or 20 mg/kg Ki16425 given subcutaneously once daily. Treatment began when the average tumor volume reached approximately 100 mm3. Mice were killed on day 48 and day 37 after treatment for UMRC3 and 786-O, respectively. Tumor volume was assessed and expressed as the mean ± S.D. (Student’s t-test; *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01). B–D, UMRC3 tumors were collected on the final day of study, fixed, and embedded in paraffin. Tissue sections were subjected to immunohistochemical analysis by using monoclonal antibodies against the nuclear Ki67 antigen and CD34 (B). The Ki67 positivity (C) and microvascular density (D) were calculated from four independent tumor sections per group and expressed as the mean ± S.D. (Student’s t-test; *, P<0.05; #, P<0.001); scale bars, 50 μm. E, production of specific cytokines secreted by xenograft tumors in animals treated with and without Ki16425. The levels of cytokine release in serum of untreated (CTL) and Ki16425-treated (Ki) mice were measured. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. (Student’s t-test; *, P<0.05). Results are representative of two independent experiments.
