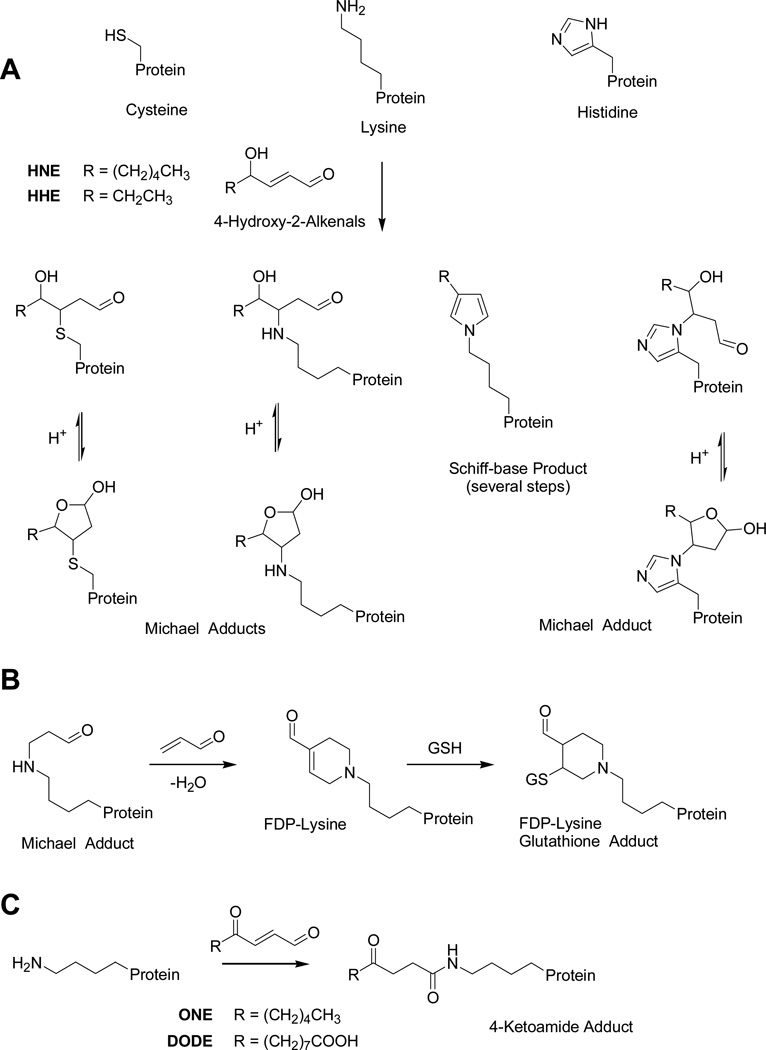
Fig. 1.
Possible modifications of proteins by aldehydic lipid peroxidation products. A) Michael-type addition and Schiff’s base formation of 2-alkenals involving nuclephilic side chains commonly found in proteins. B) Proposed formation and structure of FDP-lysine adducts. The Michael adduct of lysine reacts further with an second 2-enal (e.g. acrolein) molecule via Michael addition followed by an aldol condensation yielding the FDP-lysine adduct. FDP-lysine is an electrophile due to its 2-enal moiety and can readily react with nucleophiles, such as glutathione. C) 4-Ketoamide lysine adduct formation involving the ε-amino group of lysine and lipids with a 4-oxo-2-enal reactive moiety.