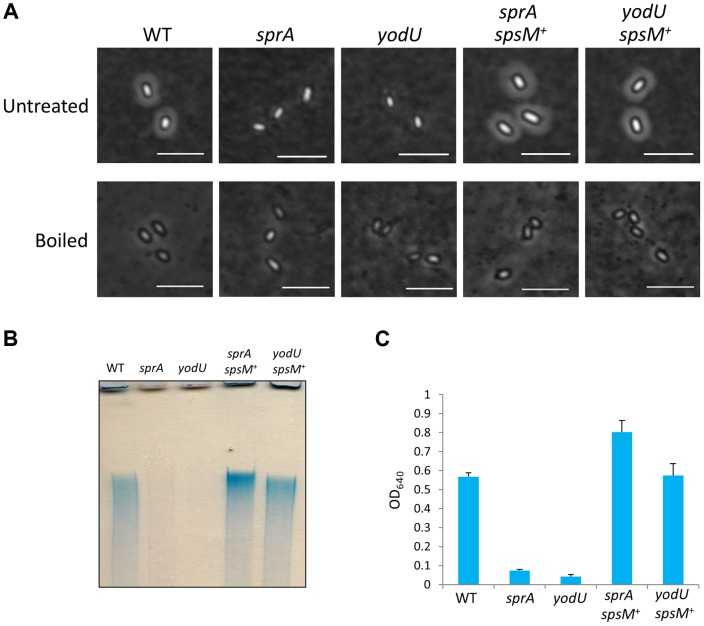
Figure 6. Analysis of B. subtilis spore surface components.
(A) Negative staining with Indian ink of the B. subtilis wild-type and mutants. The purified spores from strain 168 (WT), SPRAd (sprA), YODUd (yodU), SPRAc (sprA spsM +), and YODUc (yodU spsM +) were negatively stained with Indian ink and observed using phase-contrast microscopy. Untreated, native spores; boiled, heat-treated spores at 98°C 10 min in SDS buffer. Scale bars, 4 µm. (B) Electrophoresis of B. subtilis spore surface extracts. Spore surface extracts from strain 168 (WT), SPRAd (sprA), YODUd (yodU), SPRAc (sprA spsM +), and YODUc (yodU spsM +) were loaded onto a 5% native polyacrylamide gel. The gel was stained with Stains-All after electrophoresis. (C) Quantification of the polysaccharides in spore surface extracts. The spore surface polysaccharides from B. subtilis spores were ethanol-precipitated. The precipitants were dissolved in water and reacted with Stains-All. The amounts of polysaccharides were determined by measuring the OD640 according to the method described by Hammerschmidt et al. [32]. Error bars indicate ± standard deviations based on three independent experiments.