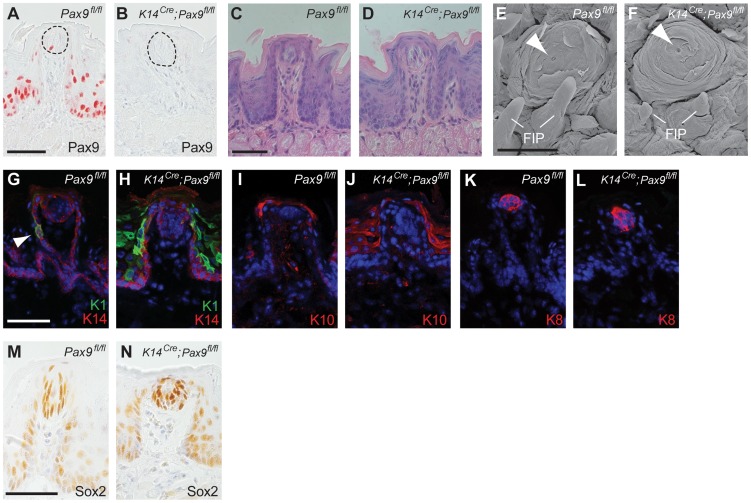
Figure 3. FUP maintenance and FUP taste bud renewal do not require Pax9 functions.
All analyses were carried out using 3–5 months old mice. (A,B) Pax9 immunostaining of FUPs. In Pax9fl/fl mice (A), Pax9 expression is detected in the FUP epithelium and in isolated taste bud cells (area of taste bud is indicated by dotted line). (B) No Pax9-positive cells are detectable in the FUP after K14Cre-mediated recombination of Pax9fl/fl. (C,D) Histological sections of FUP. Pax9fl/fl FUP (C) and K14Cre;Pax9fl/fl FUP (D) are morphologically indistinguishable. (E,F) Scanning electron microscopy images of FUP. The FUP of both Pax9fl/fl (E) and K14Cre;Pax9fl/fl (F) form taste pores (arrowhead), whereas the non-sensory FIP of the mutants (F) are hypoplastic. (G–L) Indirect immunofluorescent detection of keratins. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (G) In Pax9fl/fl mice, K14 is expressed in basal cells of the epithelium and K1 expression was seen in isolated epithelial cells of the FUP epithelium (arrowhead). (H) While K14 expression was not affected in the FUP of K14Cre;Pax9fl/fl mice, the number K1 expressing cells was strongly increased. (I,J) K10 expression is mainly restricted to the apical end of the FUP in Pax9fl/fl mice (I) whereas its expression is more extended in K14Cre;Pax9fl/fl mice (J). (K,L) K8 expression marks taste bud cells in both genotypes. (M,N) Immunohistochemical staining showing that Sox2 is expressed in mature taste buds of both Pax9fl/fl (M) and K14Cre;Pax9fl/fl (N) mice. Scale bars: 50 µm in A,C,G,M; 500 µm in E.