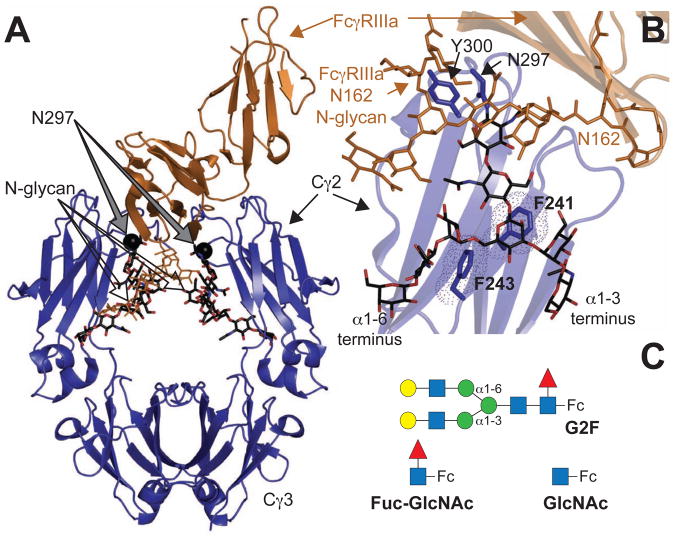
Figure 1. (A) Homodimeric IgG1 Fc.
(blue ribbon diagram) binds to monomeric FcγRIIIa (orange ribbons) (Sondermann et al., 2000). (B) Interactions between F241 and F243 amino acid sidechains stabilize the N-glycan in structures of Fc determined by x-ray crystallography. The Fc N-glycan is shown with a black stick model. An FcγRIIIa N-glycan contacts core Fc N297 glycan residues and is shown with an orange stick model (Mizushima et al., 2011) (C) Three Fc glycoforms are examined in this study: a complex-type, biantennary N-glycan containing two [13C2]-galactose (Gal) residues at the non-reducing termini (G2F-Fc), a single N-acetylglucosamine residue (GlcNAc-Fc) and Fc with a disaccharide (Fuc-GlcNAc-Fc). Carbohydrate residues are represented using the CFG convention (Varki, 2009) (GlcNAc-blue square; Gal-yellow circle; fucose (Fuc)- red triangle; mannose (Man)-green circle); α1–6 and α1–3 linkages to the branching mannose are shown that differentiate the two branches of the glycan.