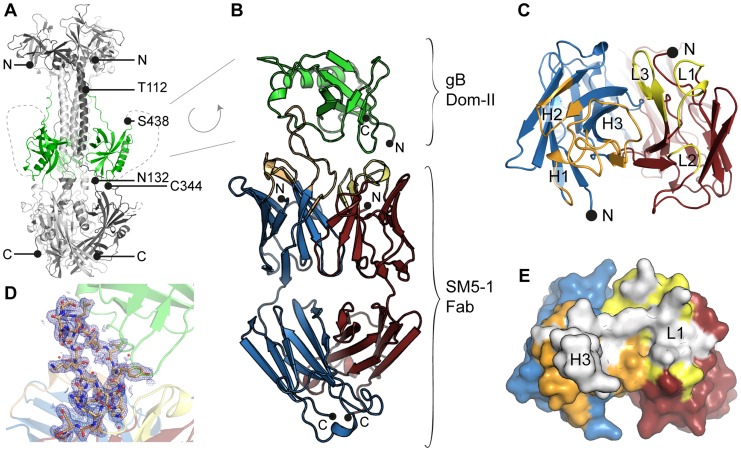
Figure 1. HCMV gB Dom-II recognition by antibody SM5-1.
(A) Trimeric model of HCMV glycoprotein B (gB) derived from the crystal structure of the homologous HSV-1 gB protein (PDB ID 2gum, [18]). Of the different gB domains, Dom-II is highlighted in green. N- (Thr-112) and C-terminal (Ser-438) amino acids of the Dom-II expression construct are labelled. Dashed lines represent regions that were not resolved in the crystal structure of HSV-1 gB and are therefore excluded from the model. (B) Cartoon representation of the Dom-II-SM5-1 Fab complex determined at an atomic resolution of 2.1 Å. Dom-II is colored in green, SM5-1 light and heavy chains are colored in red and blue, respectively. The CDR loops of the heavy chain are shown in orange and those of the light chain in yellow. Two segments of gB (residues 112–132 and 344–438) were fused together by an artificial linker segment in order to obtain a sequence-contiguous Dom-II protein [32]. (C) Top view of the antigen-binding site with the structure of Dom-II omitted in the presentation. Colors are as in (B). CDR loops are labeled L1 to L3 and H1 to H3. (D) 2mFo-DFc map contoured at 1σ and displayed within 2.5 Å around any CDR H3 atoms. Contiguous electron density is observed for the entire H3 loop in the antigen-bound structure. (E) Surface representation of the antigen-binding site of SM5-1 oriented as in (C). Shown in white is the surface area of SM5-1 that becomes buried upon antigen binding.