Figure 4. Feeding rescue experiments and abnormal cholesterol accumulation in nobo loss-of-function animals.
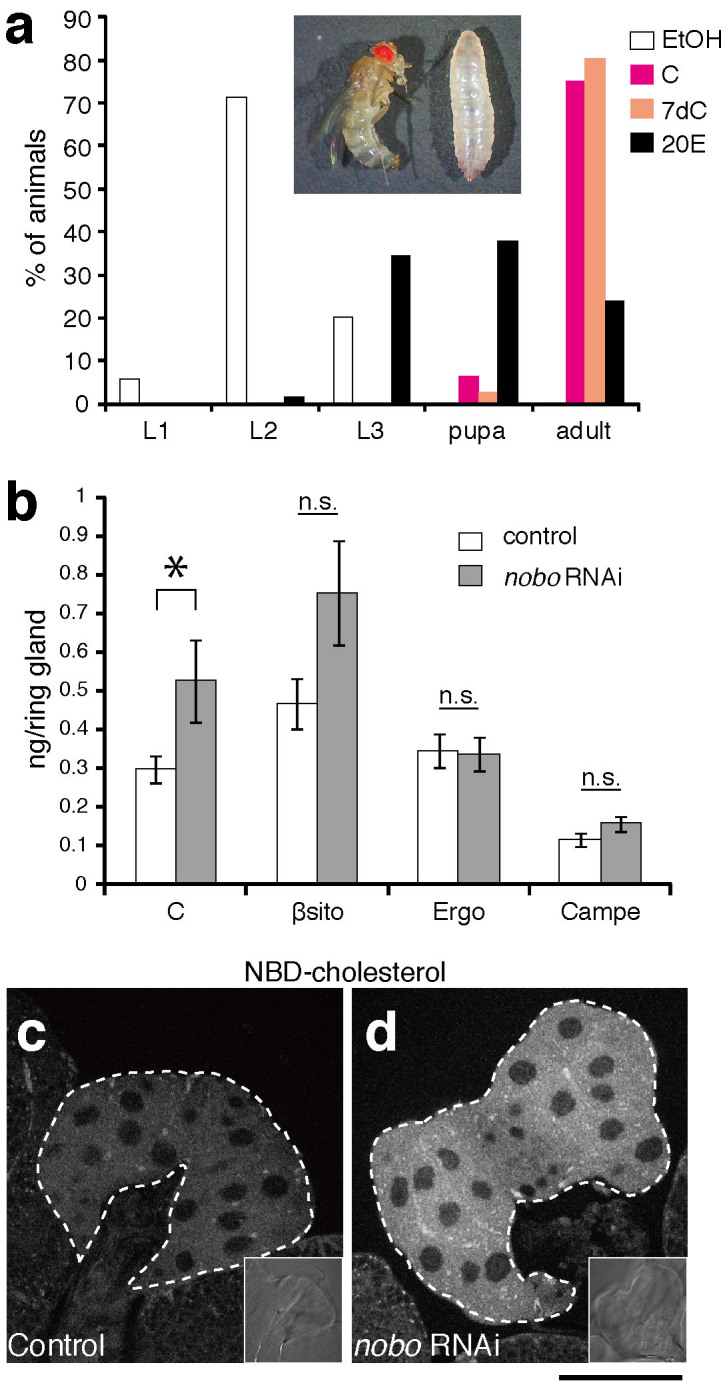
(a) Feeding rescue experiments for nobo RNAi larvae. nobo RNAi and control larvae were fed yeast paste supplemented with ethanol (EtOH, for negative control), cholesterol (C), 7-dehydrocholesterol (7dC) or 20E throughout their larval development. The concentration of each supplemented steroid in yeast paste was 0.5%(w/w) (See Methods for more details). The percentage of living animals at 240 hours AEL in each experimental condition was scored. N>30 for each experiments. Inset photo shows nobo RNAi animals at 240 hours AEL, which were raised on food with EtOH- (right) and 20E-supplemented (left) food, respectively. The larva (right) was at the 2nd instar stage. (b) Sterol amounts in the RG isolated from control and nobo RNAi larvae. C, cholesterol; βsito, β-sitosterol; Ergo, ergosterol; Campe, campesterol. 7dC amounts were under the detectable level in our experimental conditions, and thus, the 7dC data were not included in this graph. N = 10 for each genotype. *, P<0.05 with Student's t-test. n.s., not significant. Note that the higher level of β-sitosterol was observed in nobo RNAi PG cells, but the difference was not statistically significant. (c,d) Fluorescence and bright-field (inset) images of the PG from (c) control and (d) nobo RNAi animals incubated with 22-NBD-cholesterol. White dotted lines indicate the PG area. Scale bar: 50 µm.
